Chemical effect of electric current - Bee hub
advertisement

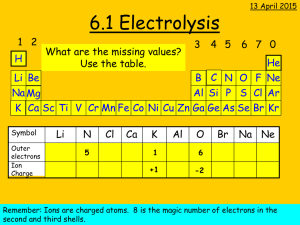
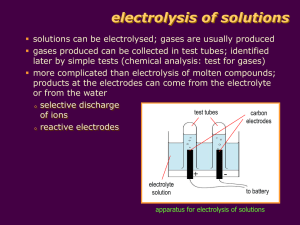
Chemical effect of electric current How things work Atom • All things around us are made up of atoms. Let us recall the model of an atom. Every atom is made up of positive and negative charged particles. The flow of charged particle inside the substance is called an electric current. The materials, which allow electric current to pass through them(in which charged particles can move freely), are conductors. On the other hand, materials, which do not allow electric current to pass through them easily, are insulators. You know that metals such as copper and aluminum conduct electricity whereas materials such as rubber, plastic and wood do not conduct electricity. Electrical conductivity • Electrical conductivity is a measure of how well a material accommodates the movement of an electric charge. Its SI derived unit is the Siemens per meter. • Good conductors have high electrical conductivity than insulators. Electrical conductivity of water • Pure water is an insulator. • Presence of small amount of impurities in water makes water a conductor of electricity. • Wet skin also becomes good conductor of electricity. Be careful not to touch the electrical appliances with wet hands. Electrical conductivity of liquids • Acid and bases dissolved in water are good conductors of electricity. • Molten salts are good conductors of electricity. • But substances that exist as liquids in room temperature like alcohols, oils are bad conductors of electricity. • The passage of electric currents through liquids causes heating just as it does in solids. Conductivity in solids and liquids • In solids like metals which are good conductors, the charge carriers are electrons. • But in liquids the charge carriers are ions.(ions are atoms or group of atoms with a positive or negative charge) Pure water does not conduct electricity because it does not form enough iron to carry the charge. Recall… • Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in which states and why? • Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten and aqueous states as the ions are not held in their fixed positions and are free to move. Solid ionic compounds do not conduct electricity as the ions are held close together in a lattice and cannot move freely. Metals can conduct electricity in solid state due to the ‘sea’ of mobile electrons. Electrical conduction Electrolytic conduction by metals and graphite by electrolytes Method of conduction Electricity is conducted by the flow of electrons from one end of the conductor to the other. Electricity is conducted by the movement of positive ions and negative ions across the electrolyte. Effect of conduction Metals and carbon remain unchanged when an electric current flows through them. The electrolytes are decomposed to form new substances when they conduct electricity. Electrolysis • The passage of an electric current through a liquid causes chemical changes. This process is known as electrolysis. • Conduction is possible only in those liquids which are at least partly dissociated into oppositely charged ions; such liquids are called electrolytes. (e.g. common salt, sulphuric acid, etc.) • +vely charged ions are called cation, and –vely charged ion is called an anion. • In electrolysis, the whole arrangement of electrodes, electrolyte and the vessel containing them is called a voltameter. What is Electrolysis? • Electrolysis is the conduction of electricity by an ionic compound, when molten or dissolved in water, leading to its decomposition. • Hence, molten ionic compounds or aqueous solutions containing free moving ions can conduct electricity and are called electrolytes. Terms to remember… • Electrolytes: – molten ionic compounds or aqueous solutions • Electrodes: metal plates or carbon rods used to conduct an electric current. – Anode: electrode connected to the positive terminal of the battery. – Cathode: electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery. • Anion: negative ion that is attracted to the anode. • Cation: positive ion that is attracted to the cathode. A Voltmeter • Two electrodes: – Cathode (negatively charged) – Anode (positively charged) • An Electrolyte • External circuit • Why is the anode positively charged and the cathode negatively charged? – The battery draws the electrons away from the anode positively charged. – The battery supplies electrons to the cathode negatively charged. What is Happening during Electrolysis? • Electrical energy chemical energy • Ions are discharged at the cathode and anode. – Cations receive electrons at the cathode. – Anions give up electrons at the anode. – The ions form atoms or molecules during the process. What Type of Reactions take place during Electrolysis? • At the cathode: – Reduction takes place as cations gain electrons. – Cu2+ + 2e- Cu • At the anode: – Oxidation takes place as anions lose electrons. – 2 Cl- Cl2 + 2e- • Hence, redox reactions take place during electrolysis. Electrolysis of molten NaCl • Solid NaCl is heated strongly until it melts (801°C). • Molten NaCl contains Na+ ions and Cl- ions. • At the cathode: – Each Na+ ion gains an electron to form a sodium atom. – Na+ (l) + e- Na (l) • At the anode: – Each Cl- ion gives up an e- to form a Cl atom. 2 Cl atoms combine to form Cl2. – 2 Cl- (l) Cl2 (g) + 2 e- • Overall reaction: 2 NaCl (l) 2 Na (l) + Cl2 (g) • Na+ ions are discharged at the cathode and Cl- ions are discharged at the anode. Try this… • Molten potassium chloride was electrolysed, using carbon electrodes. a) Write the formulas of the ions in the electrolyte. b) (i) Name the product at the cathode. (ii) Write the half equation for the reaction at the cathode. c) (i) Name the product at the anode. (ii) Write the half equation for the reaction at the anode. Industrial Applications of Electrolysis 1. Extraction of metals – To extract very reactive metals from their ores. 2. Electrolytic refining – To purify metals, such as copper 3. Electroplating The process of depositing a layer of metal on another substance using electrolysis. What is electroplating? • Electroplating (often just called "plating") is the deposition of a metal coating onto an object or metal using electrolysis.