Reaction Rates - Siverling
advertisement

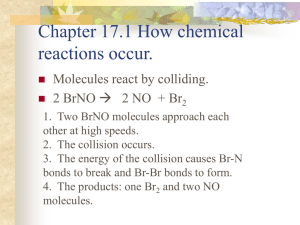
Reaction Rates Chapter 12.1 and 12.4 of A Natural Approach to Chemistry Rates of Reactions How fast does a reaction occur? Why Do We Care? Sometimes we need to slow reactions down. Sometimes we need reactions to happen quickly. Why Do We Care? How do we know if a reaction is going to occur quickly or slowly? Better yet, how can we control the rate of a reaction? Rate of Reaction Rate of Reaction - how fast a reaction occurs decrease -how quickly the amount of reactants __________ increase -how quickly the amount of products __________ Collision Theory Collision Theory – In order to react, reactant molecules must collide with each other How does this relate to reaction rates? In order to increase reaction rate, we must increase the number of collisions. Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 1) Temperature – hotter temperatures faster mean: ____________ molecules increase molecular collisions ___________ Reaction rate __________ increases Factors Affecting Reaction Rate Which of these will have more collisions? Low Concentration High Concentration Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 2) Concentration – higher concentration means: more reactant molecules _______ molecular collisions ___________ increase Reaction rate __________ increases Factors Affecting Reaction Rate Which of these will have more collisions? Low Surface Area High Surface Area Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 3) Surface Area – higher surface area means: more reactant molecules available _______ for collisions molecular collisions ___________ increase increases Reaction rate __________ Factors Affecting Reaction Rate Factors Affecting Reaction Rate increases 4) Catalyst – molecule that ____________ the reaction rate without getting used up in the reaction itself How does it do this? - It lowers the activation energy of the reaction