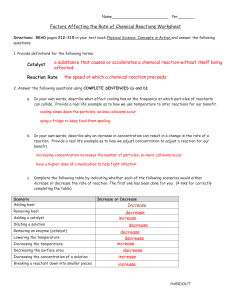
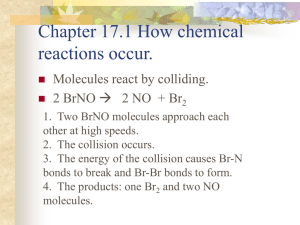
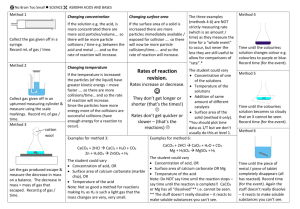
Factors that Affect Rates of Reaction
advertisement

BIG Idea of Unit Chemicals react together in predictable ways How to name ionic and covalent compounds How to balance chemical equations How to identify the common types of reactions TODAY.. What factors affect the rate at which these reactions occur? Outline Rate of reaction Collision Model 4 main Factors & Investigation: Temperature Concentration Surface Area Catalyst Rate of Reaction Rate of reaction = Quantity of product produced Time Required Chemical reactions occur at different rates Today we will consider some of the key factors that influence the rate of reaction Collision Model The rate of reaction is effected by the number of collisions of reactant molecules In order for collisions to be effective, the molecules must collide with sufficient energy Molecules must also collide with proper orientation Collision Model Factors we will examine that influence the reaction by: Increasing the number of collisions OR Increasing the fraction of collisions that will be successful INVESTIGATION How does the temperature affect rate of reaction? How does the temperature of water affect the rate at which an Alka Seltzer tablet dissolves? Reaction: NaHCO3 (s) + H2O (l) → NaOH (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) Predictions? Observations: On observation Handout Explanation: To follow! Temperature Increases energy of particles due to increase of temperature Increase speed of particles and there are more successful collisions because molecules to contact one another more readily and with harder force Therefore increased temperature = increased rate of reaction How does the concentration of a solution affect the rate of reaction? How will different concentrations (strengths) of hydrochloric acid dissolve zinc? Reaction: Zn (s) + 2HCl (l) → ZnCl2 (aq)+ H2 (g) Predictions? Observation: Fill out on handout provided Explanation: to follow! Concentration Concentration: the amount of a substance (solute) present in a given volume of solution “Packing” in more molecules increases the number of collisions Therefore a more concentrated solution = increased rate of reaction How does surface area affect the rate of reaction? How does surface area affect the rate of reaction of chalk with hydrochloric acid? (Solid chalk vs. powder chalk) Reaction: CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Predictions: Observations: on handout provided. Explanation: to follow! Surface Area If particles are in the same phase (liquid/liquid or gas/gas) then it is easy for them to mix with each other This gives particles maximum opportunity to collide But if one of the reactants is a solid, the reaction can only take place on the SURFACE of the solid The smaller the size of the particles, the greater the surface area that the reaction can take place in Therefore, smaller surface area = increased rate of reaction How does the addition of a catalyst effect the rate of reaction? Which solution will act as a catalyst effect the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide? Reaction: 2H2O2 (l) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) Predictions: ?? Observations: On handout provided Explanation: to follow!! Catalyst Substance that enhances the rate of chemical reaction without being consumed itself They decrease the amount of collision energy needed to break bonds and form new ones making the fraction of successful collisions more effective Catalysts provide an easier path for reactions to follow Note: An enzyme is a protein compound that acts as a biological catalyst Therefore presence of catalyst = increased rate of reaction Reminders: Lab tomorrow Quiz Friday on: Factors that Effect the Rate of Reaction Types of Chemical reactions Classifying types of chemical reactions Balancing chemical reactions