Science 10: Reaction Rate
advertisement

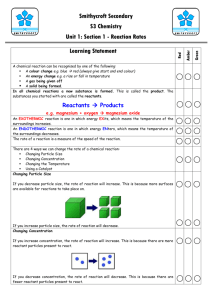
Science 10: Reaction Rate Learning outcomes 20, 21 REACTION RATE: Reaction Rate (AKA Rate of Reaction) • How quickly or slowly your reactants turn into products. Eg. From our last lab: High reaction rate Low reaction rate Factors Affecting Reaction Rate: 1) Temperature: • High temperature = Higher rate of reaction • Low temperature = Lower rate of reaction How: • Kinetic molecular theory: Particles move faster when you heat them up = more collisions Factors Affecting Reaction Rate: 2) Concentration: • Low concentration = low reaction rate • High concentration = high reaction rate How: The reactants are more likely to bump into each other Low Concentration High Concentration Factors Affecting Reaction Rate 3) Surface Area: • A lot of surface area available = high reaction rate • A low amount of surface area = low reaction rate How: • High surface area means there is a large amount of reactants available to react with. • Eg. Burning wood: A solid 2kg log burns slowly A 2kg bunch of twigs burns fast j Factors Affecting the Reaction Rate 4) Catalyst: • A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the reaction rate without being used up in the reaction. How? • A catalyst will line up molecules so that when they collide they will react. This reduces the amount of energy that is needed in a reaction Assignment Review Questions: Reaction rates and Reaction types Next class final Chem review Test on Tuesday