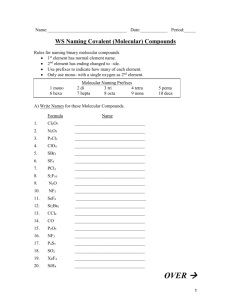
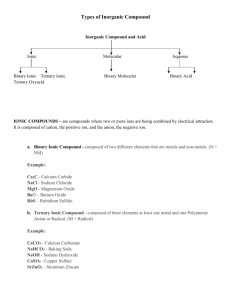
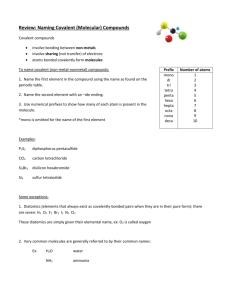
Molecular Compounds
advertisement

Molecular Compounds Molecular Compounds • Molecular Compounds form between nonmetals and nonmetals. (ex. S2O4 ) • Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons. • Neither atoms gain or lose electrons because their electronegativity values are very close. Naming Binary Molecular Compounds • To name molecular compounds, use prefixes to show how many atoms of each element there are. • Exception: do not show a prefix if the first element has only one atom. • Note: Do NOT reduce if the element ratio is not in lowest terms. • Similar to ionic compounds – last element ends in -ide Prefix mono di tri tetra penta hexa hepta octa nona deca # atoms 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Name the following molecular (covalent) compound: SiF4 1. Monosilicon fluoride 2. Sulfur fluoride 3. Monosilicon tetrafluoride 4. Silicon tetrafluoride 5. Silicon quadfluoride 0% Sil i . df l.. co n qu a te tra co n Sil i ico n id .. . M on os il 0% f. . . 0% te ... 0% fu rf lu or Su l M on os il ico n fl. . . 0% Name the following molecular (covalent) compound: SO3 Sulfur trioxide Sulfur oxide Sulfur dioxide Monosulfur trioxide 0% .. 0% ri. rt on os ul fu M Su l fu rd io xid de e 0% fu ro xi Su l fu rt r io xi d. .. 0% Su l 1. 2. 3. 4. Name the following molecular (covalent) compound: S2F6 Sulfur fluoride Sulfur hexafluoride Disulfur fluoride Disulfur hexafluoride 0% Di su lfu rh lu o r. . . ex af . .. 0% lfu rf Di su Su l fu rh ex a id .. . fu rf lu or 0% flu .. . 0% Su l 1. 2. 3. 4. Acid Nomenclature • In general, names of acids will begin with hydrogen. • If the anion does not contain oxygen, the acid begins with hydro and ends in –ic • HCl = hydrochloric acid • HBr = • HCN = Acids containing oxygen • If the acid contains oxygen, the acid does not have hydro at the start and either ends in ic or ous. • If the anion ends in –ate use –ic • HNO3 = nitric acid • If the anion ends in –ite use –ous • H2SO3 = sulfurous acid