File
advertisement
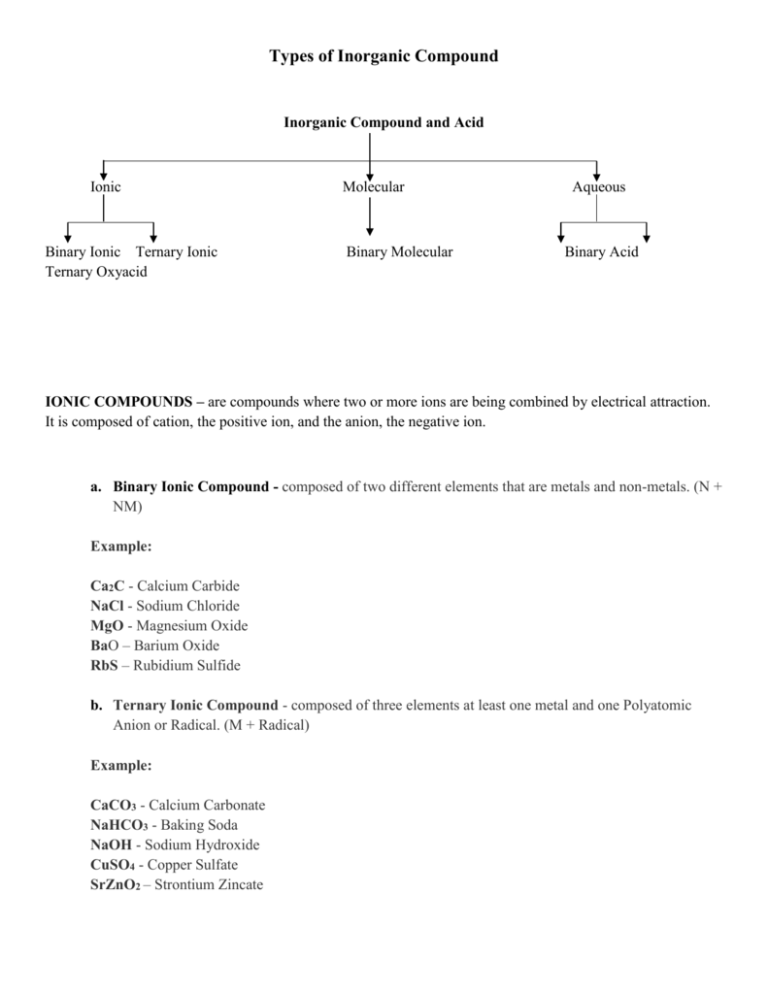
Types of Inorganic Compound Inorganic Compound and Acid Ionic Binary Ionic Ternary Ionic Ternary Oxyacid Molecular Binary Molecular Aqueous Binary Acid IONIC COMPOUNDS – are compounds where two or more ions are being combined by electrical attraction. It is composed of cation, the positive ion, and the anion, the negative ion. a. Binary Ionic Compound - composed of two different elements that are metals and non-metals. (N + NM) Example: Ca2C - Calcium Carbide NaCl - Sodium Chloride MgO - Magnesium Oxide BaO – Barium Oxide RbS – Rubidium Sulfide b. Ternary Ionic Compound - composed of three elements at least one metal and one Polyatomic Anion or Radical. (M + Radical) Example: CaCO3 - Calcium Carbonate NaHCO3 - Baking Soda NaOH - Sodium Hydroxide CuSO4 - Copper Sulfate SrZnO2 – Strontium Zincate MOLECULAR COMPOUDS – are derived from combinations of different molecules which is both nonmetals. c. Binary Molecular Compounds - composed of two elements that are both non-metals. - only inorganic compounds that are using Greek numerical prefixes. Example: NH3 - Nitrogen trihydride CO2 - Carbon dioxide SO3 - Sulfate trioxide PCl3 – Phosphorus trichloride Cl2O7 – Dichloride hexaoxide 1 2 3 4 5 mono di Tri tetra penta 6 7 8 9 10 Hexa Hepta Octa Ennea deca AQUEOUS SOLUTION - produced when a compound dissolves in water and is indicated by the symbol (aq). d. Binary Acid - water solutions of molecular compounds composed of hydrogen and another nonmetal except oxygen. (H + NM + Acid) Example: HCl(aq) - Hydrochloric Acid HF(aq) – Hydroflouric Acid HBr(aq) – Hydrobromic Acid HI(aq) - Hydroiodic Acid H2S(aq) – Hydrosulfic Acid e. Ternary Oxyacid - contains H2O and the acid forming element. Their names do not have the prefix hydro and it ends in *ic - more oxygen and *ous - less oxygen. Example: H3PO4(aq) – Phosphoric Acid H2SO4(aq)- Sulfuric Acid HClO4(aq) – Perchloric Acid H2MoO4(aq) – Molybdic Acid References: Based on discussion http://misterguch.brinkster.net/ionic.html