Basic Chemistry II
advertisement

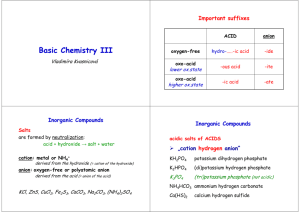
Basic Chemistry II Vladimíra Kvasnicová Exercise Add names of the elements: N Na K Ca Mg Mn Ag Cd Hg Sb nitrogen sodium potassium calcium magnesium manganese silver cadmium mercury antimony The figure is found at http://www.corrosionsource.com/handbook/periodic/periodic_table.gif (September 2007) Inorganic Compounds Make groups of compounds: Na2O, HCl, CO2, Na2O2, Ca(OH)2, KClO, HCN, HNO2, H2S, H2O2, BaO2, PbO2, H2SO3, KOH, MgSO4, NaF, NH4HCO3, HI, Al(OH)3, HIO4, CdS, MgO2, NaH2PO4 ? oxides hydroxides peroxides acids salts Inorganic Compounds Make groups of compounds: Na2O, HCl, CO2, Na2O2, Ca(OH)2, KClO, HCN, HNO2, H2S, H2O2, BaO2, PbO2, H2SO3, KOH, MgSO4, NaF, NH4HCO3, HI, Al(OH)3, HIO4, CdS, MgO2, NaH2PO4 ? oxides hydroxides peroxides acids salts Inorganic Compounds Oxides anion: O-II • acid-forming: nonmetal / oxygen use multiple prefixes (mono, di, tri,...) • base-forming: metal / oxygen use sufixes –ous / -ic or (oxidation state) • amphoteric MnO2, N2O, BaO, CO, K2O, SO2, FeO, Cu2O, CaO Inorganic Compounds Peroxides anion: O2-2 O-I • s1 elements (hydrogen and alkali metals): M2O2 • s2 elements (alkali earth metals): MO2 sodium peroxide magnesium peroxide barium peroxide potassium peroxide hydrogen peroxide lithium peroxide Inorganic Compounds Hydroxides anion: (OH)-1 • basic properties (pH > 7) • strong or weak hydroxides • metal / hydroxide anion use sufixes –ous / -ic or (oxidation state) • ammonium / hydroxide anion NaOH, LiOH, NH4OH, Fe(OH)3, Cu(OH)2, Ca(OH)2 Inorganic Compounds Acids cation: H+ (pH < 7) 1) oxygen free acids hydro-...................-ic acid HF, HCl, HBr, HI, H2S, HCN (in aqueous solutions) anion: -ide • monoprotic / diprotic acids Inorganic Compounds Acids cation: H+ 2) oxoacids the highest oxidative state per-.....-ic acid higher (or only) oxidative state -ic acid lower oxidative state -ous acid the lowest oxidative state hypo-...-ous acid anion: -ic acid → -ate -ous acid → -ite Inorganic Compounds The most important oxoacids: H2CO3 H2SiO3 H2CrO4 H3BO3 H3PO4 H2SO3 H2SO4 HNO2 HNO3 carbonic acid silicic acid chromic acid boric acid phosphoric acid sulfurous acid sulfuric acid nitrous acid nitric acid → carbonate → silicate → chromate → borate → phosphate → sulfite → sulfate → nitrite → nitrate Inorganic Compounds The most important oxoacids: HClO hypochlorous acid HClO2 chlorous acid HClO3 chloric acid HClO4 perchloric acid (or Br, I) HMnO4 permanganic acid → hypochlorite → chlorite → chlorate → perchlorate H2S2O2 H2S2O3 → thiosulfite → thiosulfate thiosulfurous acid thiosulfuric acid → permanganate Keep in mind the rules: 1. names of compounds are derived from the names of cations, anions and polyatomic ions: cation anion (NaCl = sodium chloride) 2. all binary compounds end in –ide CaO, H2O2, NaCl, HF(g), ZnS 3. binary compounds composed of two nonmetals: Greek prefixes SO2, N2O5, CO Keep in mind the rules: 4. binary compounds composed of a metal ion with fixed or variable oxidation numbers and nonmetal ion: no Greek prefixes a) -ous / -ic suffix system b) Stock system (prefered) CuCl2, CuCl, Fe2O3, FeO Keep in mind the rules: 5. ternary compounds: hydrogen cation H+ (= acid) or metal cation (= salt or hydroxide) (fixed or variable oxidation number) and a polyatomic anion (e.g. SO42- or OH1-) H2SO4 Na2SO4 NaOH Total charge of a molecule = 0 Inorganic Nomenclature Call the compounds: Na2O, HCl, CO2, Na2O2, Ca(OH)2, KClO, HCN, HNO2, H2S, H2O2, BaO2, PbO2, H2SO3, KOH, MgSO4, NaF, NH4HCO3, HI, Al(OH)3, HIO4, CdS, MgO2, NaH2PO4 Chemical reactions = chemical changes stoichiometry = the reactants combine in simple wholenumber ratios (see stoichiometric coefficients: a, b, c, d) aA+bB→cC+dD • the single arrow (→) is used for an irreversible reaction • double arrows () are used for reversible reactions chemical equilibrium = a state of a reversible chemical reaction in which the concentrations of reactatnts and products are not changing with time ie the rates of both the forward and back reactions are equal Chemical reactions equilibrium constant (K) describes the ratio of concentrations of products and reactants in the equilibrium aA+bBcC+dD K = [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b • K is constant for given reaction and fixed temperature • the definition of K is called Guldberg-Waage´s law (= law of chemical equilibrium) Chemical reactions • a chemical reaction is described by a chemical equation • the equation is balanced if substance amount of each element is the same on both sides of a chemical equation each element must be balanced in the order: metal – nonmetal – hydrogen - oxygen Conservation law (Law of conservation of mass / energy) = the total magnitude of mass (or energy or charge) remain unchanged even though there may be exchanges of that property between components of the system (the sum of masses of reactants equals to the sum of masses of products) Chemical reactions • NEUTRALIZATION = acid-base reactions H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O acid + base → salt + water • PRECIPITATION NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 → insoluble product = precipitate is formed • REDOX reactions = oxidative-reduction reactions → oxidation states of elements are changed !!! Chemical reactions oxidative-reduction reactions = REDOX reactions → oxidation states of elements are changed !!! • two changes: one element is oxidized (its ox. state raises) other element is reduced (its ox. state lowers) 2 HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 Zn0 → Zn+II zinc is oxidized (0 → +II) H+I → H0 hydrogen is reduced (+I → 0) Important terms: • reactants / products • stoichiometric coefficients • substance amount • relative atomic / molecular mass • molar mass • density • concentration (molar, percent) Exercise – add formulas • • • • • • • • • • • sodium sulfite potassium phosphate ammonium hydrogen phosphate lithium dihydrogen phosphate calcium hydrogen carbonate silver sulfide zinc sulfate potassium permanganate sodium hypobromite barium nitrate hydrargyric chloride Exercise – add formulas • • • • • • • • • • • sodium tetraborate decahydrate potassium aluminium sulfate sodium aluminium sulfate dodecahydrate ammonium carbonate calcium sulfate hemihydrate (hemi = ½) zinc sulfate heptahydrate potassium dichromate potassium magnesium fluoride ammonium magnesium phosphate led(II) chloride fluoride cupric biscarbonate difluoride (bis = twice)