Abnormal cell proliferation, differentiation and related diseases
advertisement

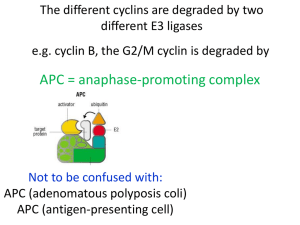
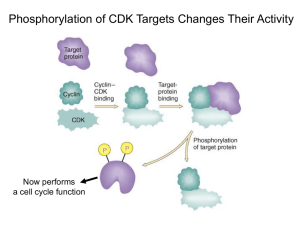
Chapter8(2) Abnormal cell proliferation, differentiation and related diseases What is cell proliferation? • Cell proliferation is a process of cell division and regeneration, which results in an increase in the cell number with exact passages of genetic information to their daughter cells. What is cell cycle? • Cell cycle is defined as a period Proliferation from the end of one division to the of eukaryotic cell division of a beginning of next proliferative cell. DNA replication Phases of the cell cycle G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase Phases of the cell cycle G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase DNA Cell Cycle Analysis For adult • Cycling cells with continuous division Embryo cells, hematopoietic cells • Differentiated cells Cardiac cells, nerve cells • Most cells Skin fibroblasts, SMCs, VECs, cells of internal organs Control of the Cell Cycle The passage of a cell through the cell cycle is controlled by proteins in the cytoplasm. These protein are: • Cyclins • Cdks (Cyclin-dependent kinases) • CKIs(Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor ) • APC (anaphase-promoting complex) Control of the Cell Cycle The passage of a cell through the cell cycle is controlled by proteins in the cytoplasm. These protein are: • Cyclins • Cdks (Cyclin-dependent kinases) • CKIs(Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor ) • APC (anaphase-promoting complex) Cyclins Kinase complex Vertebrate Yeast Cyclin CDK Cyclin CDK G1-CDK Cyclin D* CDK4 、6 Cln 3 CDK1(CDC28) G1/S-CDK Cyclin E CDK2 Cln 1、2 CDK1(CDC28) S-CDK Cyclin A CDK2 Clb 5、6 CDK1(CDC28) M-CDK Cyclin B CDK1(CDC2) Clb 1-4 CDK1(CDC28) Cyclins Kinase complex Vertebrate Yeast Cyclin CDK Cyclin CDK G1-CDK Cyclin D* CDK4 、6 Cln 3 CDK1(CDC28) G1/S-CDK Cyclin E CDK2 Cln 1、2 CDK1(CDC28) S-CDK Cyclin A CDK2 Clb 5、6 CDK1(CDC28) M-CDK Cyclin B CDK1(CDC2) Clb 1-4 CDK1(CDC28) Cyclins Kinase complex Vertebrate Yeast Cyclin CDK Cyclin CDK G1-CDK Cyclin D* CDK4 、6 Cln 3 CDK1(CDC28) G1/S-CDK Cyclin E CDK2 Cln 1、2 CDK1(CDC28) S-CDK Cyclin A CDK2 Clb 5、6 CDK1(CDC28) M-CDK Cyclin B CDK1(CDC2) Clb 1-4 CDK1(CDC28) Cdks Kinase complex Vertebrate Yeast Cyclin CDK Cyclin CDK G1-CDK Cyclin D* CDK4 、6 Cln 3 CDK1(CDC28) G1/S-CDK Cyclin E CDK2 Cln 1、2 CDK1(CDC28) S-CDK Cyclin A CDK2 Clb 5、6 CDK1(CDC28) M-CDK Cyclin B CDK1(CDC Clb 1-4 2) CDK1(CDC28) Cdks Steps in the cycle CKIs • Kip (Kinase inhibition protein): P21waf1/cip1 (cyclin inhibition protein 1)、 P27kip1(kinase inhibition protein 1)、 P57kip2 • Ink4(Inhibitor of cdk 4): P16Ink4a、P15Ink4b P18Ink4c、P19Ink4d CKIs • Kip (Kinase inhibition protein): P21waf1/cip1 (cyclin inhibition protein 1)、 P27kip1(kinase inhibition protein 1)、 P57kip2 • Ink4(Inhibitor of cdk 4): P16Ink4a、P15Ink4b P18Ink4c、P19Ink4d Degradation of cyclin B Degradation of cyclin B Cell cycle checkpoints Regulation of cell cycle by extracellular signal Growth factors Tumor • Overexpression of cyclins • Overexpression of Cdks • Deactivation of CkIs • Abnormity of checkpoints Tumor • Overexpression of cyclins • Overexpression of Cdks • Deactivation of CkIs • Abnormity of checkpoints Psoriasis What is cell differentiation? • Cell differentiation is a cellular events that gives rise to different kinds of cells with the specialized morphology, metabolism and physiological functions from the cells of the same origin. What is cell differentiation? What is cell differentiation? • Cell differentiation is a cellular events that gives rise to different kinds of cells with the specialized morphology, metabolism and physiological functions from the cells of the same origin. Control of cell differentiation – Genomic level – Transcription/post-transcription levels – Extracellular factors House-keeping genes DNA methylation↓ Differentiation-related genes DNA methylation↓ Tissue-specific genes Control of cell differentiation – Genomic level – Transcription/post-transcription levels – Extracellular factors Tumor • Low differentiation • Dedifferentiation • Retrodifferentiation • Divergent differentiation • Induced differentiation Pulmonary fibrosis Vessel injury Thrombin Myofibroblast (+) Fibroblast Deposit of collagen in lung Teratoma