Cancer and the Cell Cycle : An
overview
Ken Wu
Disclaimer
• This tutorial is a simple and conceptual guide
to the cancer module and the cell cycle
• If there are any conflicts between my slides
and the lecturers, THE LECTURER IS ALWAYS
RIGHT…
• …maybe not always but they set your exams
so if in doubt, refer back to their teaching
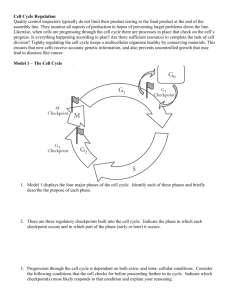
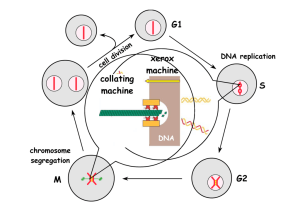
The Cell Cycle
• Most adult cells, without growth stimulus, will
go into the G0 phase of the cell cycle
• However, when a growth factor binds to its
receptor on the cell membrane, a cascade
starts and the cell prepares to enter G1
Growth stimulus
• Growth factors
– Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
– Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
• Binds to Receptors Protein Tyrosine Kinase
(RPTK)
Preparing the cascade
• Grb2 (adaptor protein) binds to
phosphorylated tyrosine
– Recruits SoS (Ras activating protein)
• SoS exchanges GDP for GTP
– Activates Ras
• Ras must be membrane bound to be active
The ERK Cascade
• RAS
– Raf
• MEK
– ERK
• Causes gene expression changes via proteins
such as c-Myc
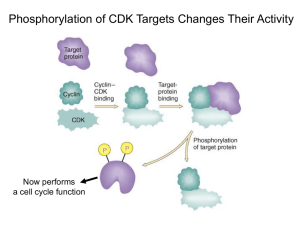
Cyclin dependent kinases (Cdk)
• Cyclically activated protein kinases
• Activation depends on
– Cyclin – Cdk interaction
– Phosphorylation
• Cyclins
– Expressed at different points in cell cycle
– Transiently expressed and degraded
Cyclin – Cdk interation
• Cdk 4,6 + cyclin D (up regulated by c-Myc)
– G0 – G1
– Also stimulates cyclin E synthesis
• Cdk 2 + cyclin E
– S phase entry
• Cdk 2 + cyclin A
– Metaphase of mitosis entry
• Cdk 1 + mitotic cyclin (cyclin B)
– Promotes mitosis
Cell cycle timing and direction
• Due to sequentially active Cdk, and synthesis
of Cdk for the next phase of cell cycle
Cyclin – Cdk function
• Phosphorylate pRb protein
• Phosphorylated pRb ‘releases’ E2F
transcription factor
• E2F is now free to facilitate gene transcription
D
pRb
Cdk4/6
E2F
pRbP
E
Cdk2
E2F
pRbPP
A Cdk2
TF
P
pRb P
B Cdk1
Mitosis
Cdk inhibition
• INK4 family
– Inhibit Cdk 4,6
– G1 phase inhibitors
• CIP/KIP family
– Inhibit all Cdks
– S phase inhibitors
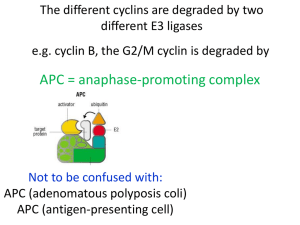
• Degradation allows cell cycle progression
The Big Picture
• G0 + EGF
– RAS, Raf, MEK, ERK, c-Myc
• Cyclin – Cdk
– D + 4,6 (G0 – G1)
– E + 2 (G1 – S)
– A + 2 (Metaphase)
– B + 1 (Anaphase)
Cancer – when it goes wrong
• Overexpressed EGFR
• Mutant RAS
– Does not dephosphorylate GTP
– Constantly bound to GTP thus constantly active
• Overexpressed c-Myc, cyclin D
• Inactive pRB
Apoptosis vs Necrosis - basics
• Necrosis
– Unregulated
– Trauma, cellular disruption
– Inflammatory response
• Apoptosis
– Regulated
– Controlled disassembly
– No inflammatory response
Apoptosis vs necrosis - process
• Necrosis
–
–
–
–
–
Plasma membrane becomes permeable
Cell swelling
Membrane rupture
Protease autodigestion
Localised inflammation
• Apoptosis
–
–
–
–
–
–
Activate death pathway
Cell shrinkage
Nuclear condensation
DNA fragmentation
Apoptotic bodies
Macrophages
Caspases
• Activation
– Proteolysis
– Cascade
• Initiator caspases
– CARD or DED domain
• Effector caspases
Caspase function
• Initiator caspase
– Activation via proteolytic cleavage
– Caspase cascade
• Effector caspase
– Cleave and inactive proteins
– Activate enzymes in apoptosis
Receptor mediated caspase activation
(extrinsic pathway)
• Fas receptor
– Fas – Fas ligand interation
– Has DD intracellular domain
• Recruits FADD
FADD
– DD of FADD attaches to DD of Fas
DED
DD
• DED domain of FADD interacts with DED domain of
caspase
• Recruits caspase 8
– Caspase cascade
– Cleaves Bid – mitochondrial pathway
• Process inhibited by FLIP
FLIP
DED
DED
Mitochondrial death pathway (intrinsic
pathway)
• Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential
– Releases cytochrome c + other factors
• Forms apoptosome complex
– Apaf 1
• Binds to cytochrome c
• CARD domain binds to CARD of caspase 9
– Caspase cascade
• Needs ATP
– Therefore energy levels decide apoptosis vs necrosis
Apoptosis modulators
• Bcl – 2 family
– Anti – apoptotic
• Bcl – 2
• Bcl –xL
– Pro – apoptotic
• Bid
• Bad
• Bax
Mechanism of apoptosis modulation
• Growth factor presence
– PI3 – K pathway
• PKB/Akt production
– Inactivates Bad, caspase 9
• Inhibited by PTEN
• Bax
– Forms pore on mitochondrial matrix
Cancer – when it goes wrong
• Overexpressed Bcl – 2
• Overexpressed PKB/Akt
• Inactive PTEN
Any questions?
• Email me at ken.wu09@imperial.ac.uk
• Visit the ICSM Year 1+2 past paper bank
Facebook group/the note bank on the ICSMSU
website
• Good luck with exams next term!