Cell Cycle and Cancer
advertisement

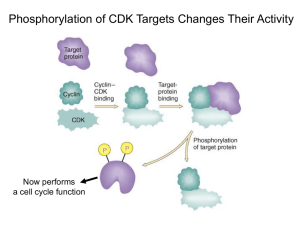
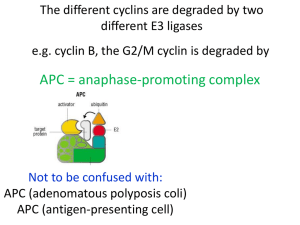
Cell Cycle and Cancer Daniel Hochhauser MILESTONES IN CELL DIVISION: TO CYCLE OR NOT TO CYCLE: A CRITICAL DECISION IN CANCER Malumbres and Barbacid Nature Reviews Cancer 1, 222-231 (2001) HALLMARKS OF CANCER Hanahan and Weinberg Cell 100,1 57-70 (2000) Cell Cycle = round of chromosomal replication in S phase followed by segregation of the replicated chromosomes into two daughter nuclei during M phase G2 / M phase transition is performed by a protein kinase conserved throughout eukaryotes MPF - protein kinase catalytic subunit p34 cdc2 - B-type cyclin G2 / M phase transition is performed by a protein kinase conserved throughout eukaryotes MPF - protein kinase catalytic subunit p34 cdc2 - B-type cyclin i.e a kinase and a cyclin RESTRICTION POINT Cells no longer require presence of serum to commit themselves to initiating DNA replication RESTRICTION POINT Cells no longer require presence of serum to commit themselves to initiating DNA replication THE RESTRICTION POINT IS ABROGATED IN CANCER Uncontrolled cell proliferation requires multi-step gene damage eg gain of function of oncogenes (accelerator) and loss of function of tumour suppressors (brakes) CDKI CYCLINS ONCOGENES when activated override brakes to cell cycle progression Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase ( cyclin D1, CDK4) Tumour suppressor genes when disabled allow accelerated cell cycle progression Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (p16, pRB) CELL CYCLE pRB E2F G1 NORMAL CELL CYCLE P pRB E2F pRB G1/S E2F NORMAL CELL CYCLE TS P pRB E2F pRB E2F NORMAL CELL CYCLE G2/M TS E2F1,DHFR…. Viral Targeting of pRb T Ag HPVE7 E1A pRB INACTIVATION OF pRB in TUMORS • • • • • • Retinoblastoma (two- hit) small-cell lung cancer soft tissue sarcoma glioblastoma breast cancer bladder carcinoma Inactivation of pRB by deletion, mutation, phosphorylation results in increased ‘free’ E2F Proliferation E2F Apoptosis POSITIVE REGULATORS OF G1 PHASE PROGRESSION CDK-CYCLIN COMPLEXES • Intrinsically inactive catalytic subunit (CDK) • Positive regulatory subunit (cyclin) • Phosphorylation of conserved threonine residue CYCLIN D • 3 Cyclin D genes • synthesised by mid-G1 phase and maximum at G1/S boundary • stimulated by growth factors • promote catalytic activity of CDK4 and CDK6 • Major substrate is retinoblastoma protein • Cells lacking pRb do not require cyclin D1 activation CYCLIN E • synthesis at late G1 phase • complexes with CDK2 NEGATIVE REGULATORS OF G1 PHASE PROGRESSION CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE INHIBITORS CIP/KIP INK4 p21cip1 p27kip1 p57kip2 p16INK4a p15INK4b p18INK4c p19INK4d INK4 CDKI • specifically target CDK’s • INK4 proteins sequester cdk4/6 into complexes liberating cip/kip proteins • ability to arrest in G1 dependent on intact pRb • p16 and p19 alternative transcripts • p16 – familial malignant melanoma – ectopic expression results in G1 arrest cell cycle arrest Cip/Kip CDKI • p21= waf1=Sdi1 inhibits cyclin/CDK function through cell cycle Cip/Kip CDKI • p21= waf1=Sdi1 inhibits cyclin/CDK function through cell cycle • universally inhibits cdks Cip/Kip CDKI • p21= waf1=Sdi1 inhibits cyclin/CDK function through cell cycle • universally inhibits cdks • activated by p53 -critical in induction of cell cycle arrest CELL CYCLE GENE ALTERATIONS IN CANCER • pRb deletion / mutation • p16 deletion / mutation CELL CYCLE GENE ALTERATIONS IN CANCER • pRb deletion / mutation • p16 deletion / mutation • p27 inactivation (methylation) CELL CYCLE GENE ALTERATIONS IN CANCER • • • • • • pRb deletion / mutation p16 deletion / mutation p27 inactivation (methylation) cyclin D1 overexpression cyclin E overexpression CDK4 overexpression Keyomarsi et al N Engl J Med. 2002 p53 MDM2 CELL CYCLE PROGRESSION SERINE-15 P ATM p53 CELL CYCLE ARREST MDM2 Increasing endogenous CDK inhibition Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 20S proteasome Histone deacetylase inhibitors Altering cyclin levels Flavopiridol Cyclin D Rapamycin (CCI-779) Cyclins D and A Direct inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases Flavopiridol CDK1, 2, 4 UCN-01/staurosporine CDK1, 2, 4, PKC, chk1 Cyclin D1overexpression, pRB deletion Hanahan and Weinberg