Overview of Insulin Therapy in Diabetes
advertisement

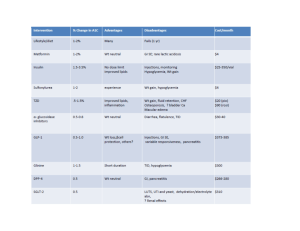
Dr Stanley Ngare Pharmacology of Types of insulin available Various routes of delivery & factors that affect absorption Patient and provider barriers Treatment should be individualised Challenges in monitoring blood glucose Complications of insulin therapy. Pre 1922- Type 1 DM: Was an acute terminal illness Insulin changed this: Saved lives = chronic illness Now: Helps achieve glycemic control hence delay or prevent microvascular complications ?prevent macrovascular complications Rapid acting Analogues (insulin like) Short acting /soluble/ regular Intermediate acting 1. 2. 3. Isophane (NPH- Neutral Protamine Hegadorn) Long acting (Analogues) 4. Glargine Detemir Single most important “ medical” barrier to glycaemia : ▪HYPOGLYCEMIA Single most important “ Patient &provider barrier” to glycaemia: PSYCHOLOGICAL “ INSULIN RESISTANCE” All people with Type 1 Diabetes Many Type 2 Diabetic patients Pregnancy Inpatient care Calculate the TDD • Type 1 (0.6) UI kg/day • Type 0.2-0.3UI kg/day Some conditions may require higher or less doses e.g obesity, puberty, hypoglycemia unawareness. Progressive adjust insulin to target SMBG ( Glucometer) • Essential tool Appreciation Mr Michael Brown -CDE