Chapter-5-Sources-of-Energy
advertisement
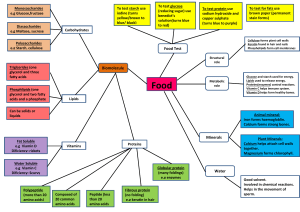
Sources of Energy Higher Human Biology Lesson Aims • To compare the differences between mono-, di- and poly-saccharides • To examine the structure of lipids and their various roles in cells and organisms • To study protein degradation and their use as an alternative respiratory substrate Monosaccharides • Made up of six-sided unit • Described as reducing sugars Disaccharides • Made of two monosaccharides joined together Polysaccharides • A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate composed of many monosaccharide molecules joined together. • ALL CARBOHYDRATES ARE RICH SOURCES OF ENERGY Lipids Includes fats, oils, phospholipids and steroids. Contain C, H and O. Triglyceride (Simple lipid) Phospholipids Steroids Roles of Lipids • • • • • • Energy store Thermal and nerve insulation Fat pads Vitamin transport Hormones Major components of the plasma membrane Proteins • Proteins broken down into amino acids. • Excess amino acids cannot be stored in the body. • They are deaminated into urea and organic compounds. • These organic acids enter the respiratory pathway to produce some ATP Marathon Running • In the first few minutes the body uses glucose from muscle glycogen • Blood glucose mainly from liver glycogen is used for the next 30 minutes • As glucose supplies decrease fatty acids become the energy supply The Facts You Need To Know • page 3 • from “carbohydrates may be ….” • to “fat pads beneath the skin…”