Chapter 2 Outline – Chemical Basis of Life
advertisement

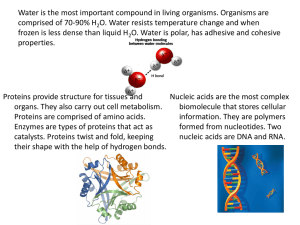
Name: Test Date: Chapter 2 Outline – Chemical Basis of Life – Part 1 I. Introduction A. Why is it important to have a basic knowledge of chemistry when studying physiology? B. Biochemistry: Deals directly with the processes that underline life activities such as: II. Basic Chemistry A. All matter is composed of ________. Matter is…..? B. 96% of the material in the human body is composed of: a. There are _____ major elements. b. There are _____ trace elements. C. Atoms: a. Subatomic Particles 1. 2. 3. b. Significance of valence electrons…. D. Compounds: E. Molecules: III. Chemical Bonds A. Ionic B. Covalent C. Hydrogen IV. Properties of Water *Body’s most abundant compound – makes up ~____% of the body’s weight. *Important in transporting substances in the body. *Carries waste materials. *Absorb and transport heat. A. Strong polarity B. High specific heat C. High heat of vaporization D. Cohesion V. Electrolytes: Examples: Cation: Anions: A. Acids B. Bases C. pH Scale: Represents the concentrations of_______________ a. 7 = b. 0-6 = c. 8-14 = D. Buffers VI. Biomolecules A. Carbohydrates a. Made from: _________________ (simple sugars), _______________, and _________________ (complex sugars) b. Structure: i. Contain the elements: ii. Monosaccharides form short carbon chains 1. ex: ____________ chemical formula:___________ c. Function: i. Provides __________ for cellular activities ii. Structural role in _____ and _____ B. Lipids a. Include ________, ________________, steroids and _____________. b. Water insoluble c. Fats/Triglycerides i. Structure: ii. Function: d. Phospholipids i. Structure: ii. Function: e. Steroids i. Ex: Cholesterol – found in _______________, provides stabilization for the cell. ii. Other steroids in the body include: f. Prostaglandins C. Proteins a. Have a wide range of functions in the body such as: b. Building blocks of proteins are: c. Enzymes: D. Nucleic Acids: a. Form genes and take part in __________ synthesis b. Building block of nucleic acids: i. Structure of nucleotide: c. Two major types: VII. Metabolism A. Metabolism: All the chemical reactions that take place in our body’s cells a. Catabolism: Chemical reaction that ___________ large molecules into smaller units. This type of reaction __________ energy. Also called a __________ reaction because a water molecule is added for the reaction to occur. b. Anabolism: Chemical reaction that __________ smaller molecules to form __________ molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). This type of reaction _________ energy, usually in the form of ______. Also called a _______________ reaction because a water molecule is removed during the reaction.