3.2 starscak
advertisement

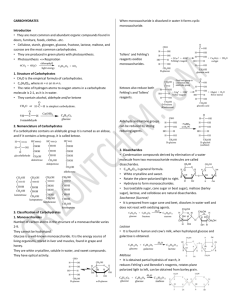
3.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Nolan Starczak 3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Compounds containing carbon that are found in living organisms (except hydrogen carbonates, carbonates and oxides of carbon) are considered organic. - This means pretty much anything containing a carbon is an organic compound, while things like water (H2O) and other mineral based compounds are considered to be inorganic. 3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from diagrams showing their structure. In this section you will have to be able to identify and draw the generalized structures of an amino acid and a fatty acid. Also you will need to be able to identify and draw both glucose and ribose. See pictures of all at the bottom. 3.2.3 List three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. -Monosaccharides are the smallest of the carbohydrates and are considered a sugar, they serve as fuel for the bodies cells. Three examples of a monosaccharide are glucose, galactose and fructose. -Disaccharides are formed by two monosaccharides covalently bonding to each other in a dehydration reaction. Three examples of disaccharides are maltose, lactose and sucrose. -Polysaccharides consist of up to thousands of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic linkages. Polysaccharides serve as storage material or cellular building structures. Three examples of a polysaccharide are starch, glycogen and cellulose 3.2.4 State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. -Glucose is an essential in animal cells since it is the cells main source of energy. Since lactose contains the monosaccharide glucose in it, lactose can be broken down in order to obtain glucose. This is only done if little glucose is present since it is not as efficient. Animals store sugar for short term use in the form in glycogen. Glycogen molecules are stored mainly in muscle and liver cells. -Fructose is equivalent of glucose in plants in that it is the main carbohydrate found in plants, main use in monosaccharide form is energy. Plants generally transport carbohydrates throughout their structure in the form of sucrose. Energy is stored within plants in the form of starch, usually in the form of amylase. 3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. These monomers are connected and broken apart with the aid of dehydration and condensation reactions. In a dehydration reaction two monomers are bonded when a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a hydrogen (-O) are removed. These two groups are removed and form water and the two monomers bind together at the same site. A hydrolysis reaction is the basically the reverse of a dehydration reaction. Bonds between monomers are broken with an addition of water molecules to each. A picture of this can be seen at the bottom. 3.2.6 State three functions of lipids. -Lipids can be used for long term energy storage in the form of fat. One gram of fat contains more then twice as much energy that is in a gram of starch. -Phospholipids can be used to make due to the ambivalence of the phospholipids head and tails towards water. The heads are hydrophilic (water loving) and the tails hydrophobic (water fearing) which allows them to create a water tight membrane. Picture of this can be seen at the bottom. -Lipids are also structural components in steroids, such as cholesterol. Sex hormones are steroids produced from cholesterol. 3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage. 3.2.2 Glucose 3.2.5 Energy stored in lipids is much more efficient per pound than carbohydrates. Because plants are virtually immobile than can cope with the bulkier energy storage of carbohydrates like starch. Animals on the other hand use lipids for energy storage due to the fact it is more advantageous to have a compact energy which allows them more movement. Energy is also much more readily available in the form of carbohydrates than it is with lipids. Ribose 3.2.6 3.2 Key Vocab Terms: -Carbohydrate -Lipid -Protein -Organic Compound -Monosaccharide -Disaccharide -Condensation Reaction -Hydrolysis Reaction -Inorganic Compound -Polysaccharide