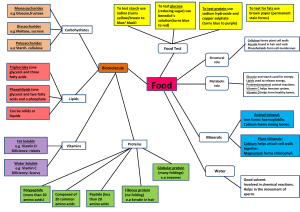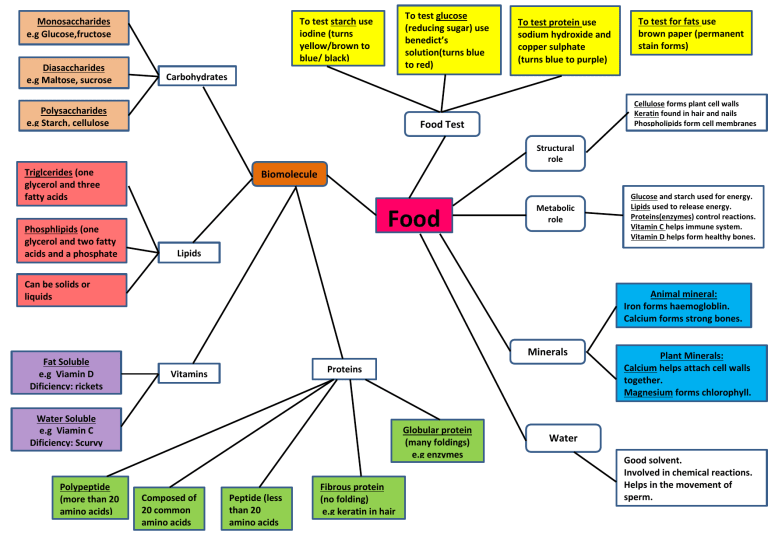
Diasaccharides e.g Maltose, sucrose To test glucose (reducing sugar) use benedict’s solution(turns blue to red) To test starch use iodine (turns yellow/brown to blue/ black) Monosaccharides e.g Glucose,fructose To test protein use sodium hydroxide and copper sulphate (turns blue to purple) To test for fats use brown paper (permanent stain forms) Carbohydrates Polysaccharides e.g Starch, cellulose Cellulose forms plant cell walls Keratin found in hair and nails Phospholipids form cell membranes Food Test Structural role Triglcerides (one glycerol and three fatty acids Phosphlipids (one glycerol and two fatty acids and a phosphate Biomolecule s Food Metabolic role Glucose and starch used for energy. Lipids used to release energy. Proteins(enzymes) control reactions. Vitamin C helps immune system. Vitamin D helps form healthy bones. Lipids Can be solids or liquids Animal mineral: Iron forms haemogloblin. Calcium forms strong bones. Lipids Lipids Fat Soluble e.g Viamin D Dificiency: rickets Minerals Proteins Vitamins Water Soluble e.g Viamin C Dificiency: Scurvy Polypeptide (more than 20 amino acids) Globular protein (many foldings) e.g enzymes Composed of 20 common amino acids Peptide (less than 20 amino acids Fibrous protein (no folding) e.g keratin in hair Plant Minerals: Calcium helps attach cell walls together. Magnesium forms chlorophyll. Water Good solvent. Involved in chemical reactions. Helps in the movement of sperm.