2.3 carbohydrates and lipids
advertisement

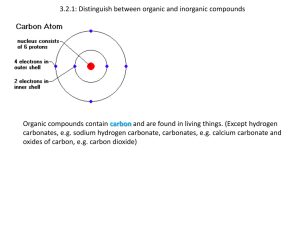
2.3: Carbohydrates & Lipids Carbohydrates You have 30 seconds to write down EVERYTHING you know… Investigating starch Download the method from moodle. Complete experiment HWK Evaluate the method using the IB marking criteria. Comparing the energy storage of carbohydrates & lipids Polysaccharides Three examples, all formed from glucose. Starch Glycogen Cellulose Formed from alphaglucose. Condensation between C-1 and C-4. Each alpha glucose is in the same position. Results in a curved structure Forms a helix, using hydrogen bonds. Formed from alphaglucose. Condensation between C-1 and C-4. Very similar to starch, but the chains form branches, resulting in a globules. Formed from betaglucose. Condensation between carbon-1 and carbon-4. Each beta glucose added to the chain is 1800 to the previous one. Results in a straight chain. Form bundles, using hydrogen bonds. Storage in plants Animals & some fungi, stored in the liver & muscles. Very strong, plant cell walls Lipids Triglycerides are formed from the condensation between three fatty acids and one glycerol. Triglycerides are present in adipose tissue (fat in humans) and oils in sunflower seeds. Fats are liquid at body temperature, solid at room temperature. Oils are liquid at both temperatures. See fig. 7, pg. 78 for diagram of condensation reaction. The bond between an acid (fatty acid) and the OH- (glycerol) is an ester. Useful for energy storage. Energy can be released by aerobic Energy storage Lipids = long term storage Carbohydrates = short term storage Why? 1. Lipids release twice as much energy per gram 2. Lipids have secondary roles e.g. insulation, shock absorber Glycogen is the short term energy store of carbohydrate. Glycogen can be rapidly broken down into glucose and transported in the blood. Glucose can then be used for aerobic or anaerobic respiration. Fatty acids Can be saturated, monounsaturated or even polyunsaturated Most fatty acids have between 14 – 20 carbon atoms. See fig. 12, pg. 82 for a diagram showing the three forms of fatty acids. The two forms of unsaturated fatty acids Cis-fatty acids, hydrogen atoms on the same side of the carbon atoms either side of the double bond. Trans-fatty acids, hydrogen atoms on opposite sides of the carbon atoms either side of the double bond. Cis Bend in the hydrocarbon means cis-fatty acids cannot be ‘packed’ so easily lower melting point. Liquid at room temp. = oils Trans No bend, so can be tightly packed together high melting point. Solid at room temperature = fats. Read Health risks of fats, pg. 83 - 85 Evaluate the evidence and the methods used to obtain evidence for health-claims made about lipids. Complete data-based questions.