DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS
advertisement
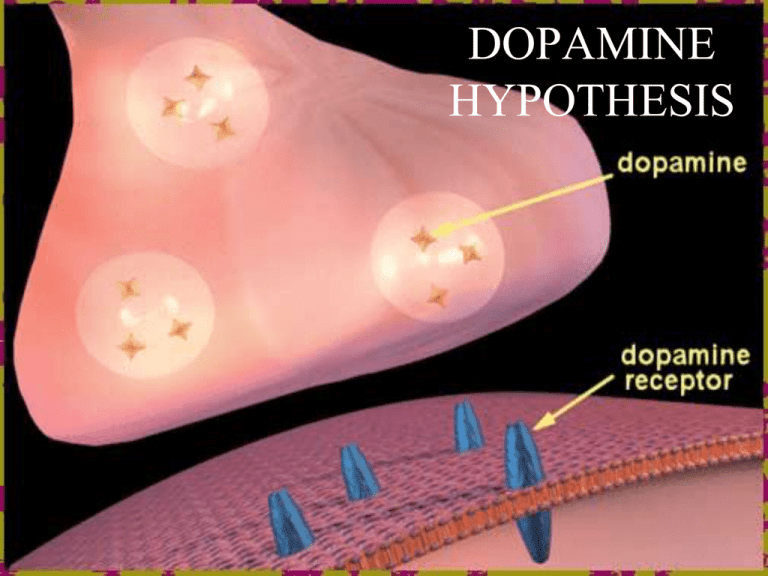
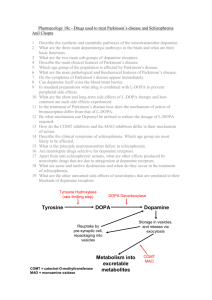
DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson your goal is to be able to • Describe the role of Dopamine (DA) in schizophrenia and you should be able to • Outline evidence to support this hypothesis You could even be able to • Evaluate the Dopamine Hypothesis Lets remind ourselves how neurotransmitters work 1 5 2 4 3 Lets remind ourselves how neurotransmitters work DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS The Dopamine hypothesis states that the brain of schizophrenic patients produces more dopamine than normal brains. Evidence for this comes from studies with drugs post mortems pet scans Dopamine Hypothesis Although the original Dopamine Hypothesis states that the brain of schizophrenic patients produces more dopamine than the brain of a “normal” person. It is now thought that schizophrenics have an abnormally high number of D2 receptors. Normal Level of Dopamine In The Human Brain Elevated Level of Dopamine In The Brain of a Schizophrenic Patient (specifically the D2 receptor) Neurons that use the transmitter ‘dopamine’ fire too often and transmit too many messages. There may be an excess of DA receptors at the synapse in schizophrenics Lowering DA activity helps remove the symptoms of schizophrenia ROLE OF DRUGS Amphetamines (agonists) lead to increase in DA levels Large quantities lead to delusions and hallucinations If these drugs are given to schizophrenic patients their symptoms get worse Randrup et al Rats given amphetamines developed schizophrenia type symptoms Parkinson’s disease • Parkinson’s sufferers have low levels of dopamine • L-dopa raises DA activity • People with Parkinson's develop schizophrenic symptoms if they take too much L-dopa –Chlorphromazine (given to schizophrenics) reduces the symptoms by blocking D2 receptors Post-mortems Seidman (1990) Post-mortem (after death) examinations have found that people with schizophrenia have a larger than usual number of dopamine receptors. Increase of DA in brain structures and receptor density (left amygdala and caudate nucleus putamen) Concluded that DA production is abnormal for schizophrenia PET SCANS Lindstroem et al (1999) • Radioactively labelled a chemical L-Dopa • administered to 10 patients with schizophrenia and 10 with no diagnosis • L-Dopa taken up quicker with schizophrenic patients • Suggests they were producing more DA than the control group PET Scans Gjedde and Wong (1987) There are more than twice as many dopamine receptors in schizophrenics compared to controls. Farde et al. (1990) There is no difference in the number of dopamine receptors between schizophrenics and controls. What is the main strength of a PET scan? What conclusions can be drawn from the research findings? Which Came First? Chickens hatch The Chicken or the Egg? from eggs, but a mother chicken must keep an egg warm in Schizophrenia or Faulty order for Chemicals? it to hatch Faulty chemicals cause schizophrenia but schizophrenia may cause faulty chemicals Drugs may influence other systems that impact on schizophrenia so we cannot be 100% sure about their effects There are lots of problems with the dopamine hypothesis! • Read your handout carefully. • There is a lack of correspondence between taking phenothiazines and signs of clinical effectiveness. It takes 4 weeks to see any sign that the drugs are working when they begin to block dopamine immediately. We cannot seem to explain this time difference. • It could be that the development of receptors in one part of the brain may inhibit their development in another. Other EVALUATION POINTS • Type 1 cases respond well to conventional anti-psychotic drugs. Drugs such as CHLOPROMAZINE: Only effective at relieving the Positive Symptoms of the Illness. • Not good at explaining negative symptoms. Therefore suggested that Type 2 is related to a different kind of abnormality such as brain structure. • PET scans have suggested that drugs did not reduce symptoms of patients diagnosed with disorder for 10 yrs or more • There may be other neurotransmitters involved. • Possible that social and environmental factors trigger the condition. ACTIVITY • Describe and evaluate the dopamine hypothesis as an explanation of schizophrenia • You must comment on how the evidence you use supports or challenges the DA hypothesis. • You should comment on evidence both for and against the hypothesis. • You could use your own skills and knowledge to make additional critical and evaluative points.