Heating Curve - Liceo Statale Aprosio
advertisement
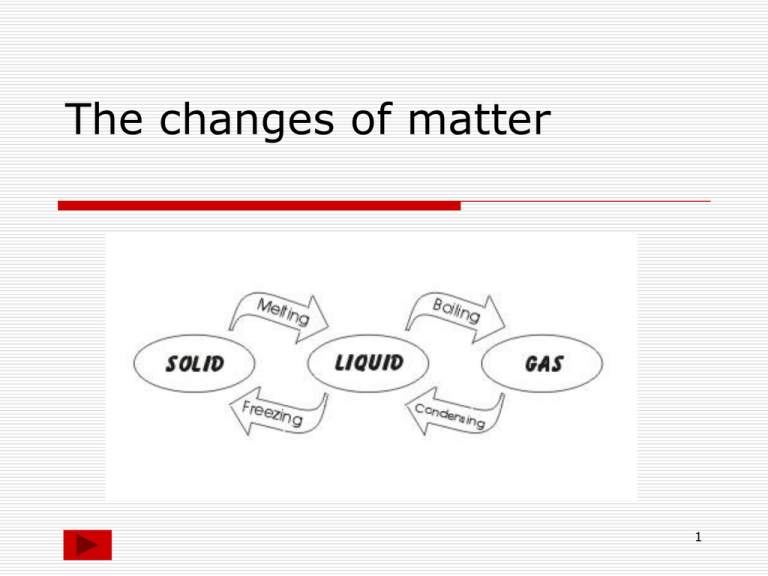
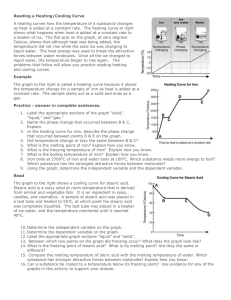
The changes of matter 1 2 Heating Curve Once the melting point and the boiling point are reached the temperature remains constant When we heat a solid, its temperature increases, the substance melts at the melting point and becomes a liquid When we heat a liquid, its temperature increases, the substance boils at the boiling point and becomes a gas 3 Heating curve for iron Different substances have different melting points and different boiling points but the shapes of their heating curves are very similar this is the heating curve for iron. The melting point of iron is 1500 °C 2750 °C The boiling point of iron is 1500 °C 2750 °C 4 Cooling Curve Once the condensation point and the freezing point are reached the temperature remains constant When we cool a gas, its temperature decreases, the substance condenses at the condensation point and becomes a liquid When we cool a liquid, its temperature decreases, the substance freezes at the freezing point and becomes a solid 5 Cooling curves for stearic acid and salol freezing point Cooling curve for salol Different substances have different condensation points and different freezing points but the shapes of their cooling curves are very similar freezing point Cooling curve for stearic acid 6 Changes of matter Getting colder gas boiling condensing liquid melting Getting hotter freezing Solid 7 Look at the table below and write sentences to describe the states of substances solid The substance will be a liquid if the temperature is between above below the boiling point the melting point the melting point and the boiling point gas 8 ANSWER THE QUESTIONS WHEN A LIQUID IS HEATED AND IT BOILS its particles lose their order and become completely free to form a gas or vapour Its particles gain energy and move faster Energy is needed to overcome the attractive forces in the liquid TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE 9 ANSWER THE QUESTIONS WHEN A LIQUID IS COOLED AND IT FREEZES its particles lose energy and so become more tightly attracted to one other at the freezing point the forces of attraction are sufficient to remove any remaining freedom and the particles come together to form the ordered solid arrangement. TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE 10 When we cool a gas, its temperature decreases, the substance condenses at the condensation point and becomes a liquid When we cool a liquid, its temperature decreases, the substance freezes at the freezing point and becomes a solid Once the condensation point and the freezing point are reached the temperature remains constant For the same substance Tmelting equals Tfreezing and Tboiling equals Tcondensation The Tc and Tf temperatures change for different substances (Tc of water is different from Tc of alcohol) 11