IAN 28-29
advertisement
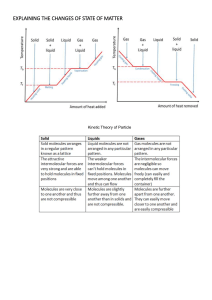
Chemical Properties of Matter IAN pg. 29 Main Ideas 1. Freezing Point 2. Melting Point 3. Evaporation 4. Sublimation 5. Boiling Point 6. Condensation 7. Dew Point Objective Identify chemical properties and changes in matter using demonstrations, notes and collaboration. II. Changes of states of matter are physical changes. A. Freezing Point: The temperature when a Liquid turns into solid. B. Melting Point: The temperature when a Solid turns into a liquid. C. Evaporation: liquid to a gas. Occurs over a wide range of temperatures. D. Sublimation: Solid to a gas. E. Boiling Point:. Specific Temperature at which a Liquid turns into a gas. F. Condensation: Gas to a liquid. Dependent upon temperature & humidity. G. Dew Point – The temperature at which condensation will occur. (rain) Section 2-3 III. Identifying substances A. Some physical properties identify substances better than others. Good identifiers: density, heat conductivity, solubility, electric and magnetic properties. B. Separating mixtures 1. Filtering: Sand from water 2. Drying: Salt from water 3. Magnetic: Metal from non-metal Sewage treatment plants use mixture separation. IAN page 28 PHASE CHANGES OF MATTER CONCEPT MAP Create a concept map showing the relationship between changes in states of matter using: Evaporation, Boiling Point, Freezing, Freezing Point, Dew Point, Condensation, Sublimation, Melting, Melting Point Sublim ation GAS ES SOLI LIQUI DS