Phase Changes
advertisement

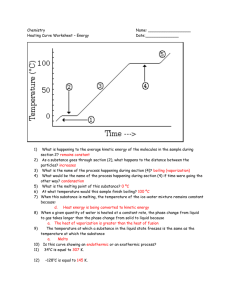
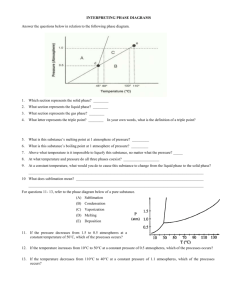
Phase Changes Phase Changes exothermic sublimination vaporizing melting solid liquid freezing endothermic gas condensing Phase changes and their enthalpy changes. Heating Curve Heating Curve of Water Quantitative Aspects of Phase Changes Within a phase, a change in heat is accompanied by a change in temperature which is associated with a change in average Ek as the most probable speed of the molecules changes. q = (specific heat )(amount)(ΔT) During a phase change, a change in heat occurs at a constant temperature, which is associated with a change in Ep, as the average distance between molecules changes. q = (amount)(enthalpy of phase change or ΔH) Heats of Fusion and Vaporization Problem • How much energy is transferred when 125 g of water are converted from 25oC to 70oC? to 120oC? ΔHvap = 2.26 kJ/g ΔHfus = 0.33 kJ/g sp.htice = 2.09 J/g oC sp.htwater = 4.18 J/g oC sp.htsteam = 2.10 J/g oC Phase Diagrams Fusion Curve critical point Pressure melting 1 atm freezing Liquid Solid normal boiling pt. normal melting pt. Sublimation Curve sublimation deposition triple point vaporization condensation Gas Temperature Vapor Pressure Curve Phase diagrams for CO2 and H2O. CO2 H 2O