Matter-Phase Changes - Madison Public Schools
advertisement

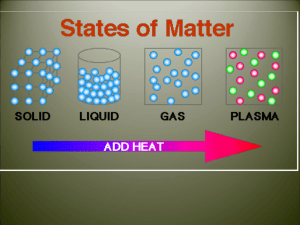
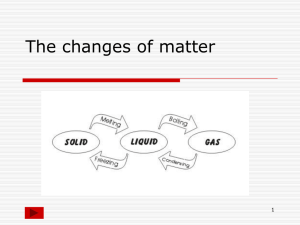
States of Matter Phase Change Science 6 Water • Water exists on our planet in three states. • Ice, water, and water vapor • What causes water to be in one phase or another? ENERGY • When energy is added to a substance that energy causes the particles in the substance to move faster and farther apart. • What happens to the particles when energy is taken away from a substance? Phase Change • Energy content is responsible for the different phases of matter. • Matter can be made to change phase when energy is added to or taken away from a substance. DO NOW Page 2 in notebook • Observe the ice cube. • Describe everything you see happening. • Why is this happening – be specific. – Use knowledge you already have to explain this process! Melting- Solid to Liquid • Melting is the changing of a solid to a liquid when the substance absorbs heat energy. • Melting Point – Water 0° C. 32° F – Table salt 801° C. 1474 ° F – Diamond 3550° C. 6422 ° F click Melting Point? • What is a melting point? Melting Point? • What is a melting point? • It is the precise temperature at which a particular substance melts changing from a solid to a liquid when the substance absorbs heat energy. • ! Phase Change Animation Phase Change Diagram If something melts, then it can freeze! Freezing- Liquid to Solid • Opposite of melting: liquid changing to a solid is freezing. • Freezing occurs when a substance loses heat energy. • The freezing point of a substance is equal to the melting point! Water Molecules Freezing • click Questions • What is a Freezing Point? • What might someone find interesting about the melting point and freezing point of a particular substance? Questions • What is a Freezing Point? • It is the precise temperature at which a particular substance freezes! • What might someone find interesting about the melting point and freezing point of a particular substance? • They are the same temperature! More Questions • What is melting? – Turning from a _______________ to a ______________ due to _________ of energy. • What is freezing? – Turning from a _______________ to a ______________ due to __________ of energy. More Questions • What is melting? – Turning from a ____solid_________ to a ______liquid____ due to _gain__ of energy. • What is freezing? – Turning from a ___liquid___ to a __solid__ due to _loss_ of energy. Vaporization- Liquid to Gas • Vaporization is the changing of a liquid to a gas when the substance absorbs heat energy. • Vaporization occurring at the surface of a liquid is called evaporation. The Water Cycle Vaporization a.k.a. Boiling • If enough heat energy is applied to a substance particles inside the liquid can change to gas. • These particles travel to the surface of the liquid and then into the air. This process is called boiling. Boiling Point • Boiling Point – temperature at which a substance boils. – Water 100° C. 212° F. – Table salt 1413° C. 2575° F. – Diamond 4827° C. 8720° F. Water Phase Change Graph What is the difference in the amount of energy need to melt and to boil? MORE Questions • What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? MORE Questions • What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? – Evaporation happens only at the surface – Examples – lake, ocean, perspiration – Boiling, or vaporization, is when the particles within a liquid take in enough heat (energy) to become a gas. “Rolling boil” Condensation- Gas to Liquid • Gases can change phase also - in a gas to liquid phase change. • A substance in the gas phase that loses heat will change to a liquid. This is called condensation. Condensation • Water vapor in surrounding air loses heat energy when it comes in contact with the cold glass. Water vapor condenses and becomes liquid drops of water. Condensation in the Water Cycle THINK!!! If water vapor in the air must condense to form a cloud, then a cloud is made of ____________? Yes, More Questions! • What is condensation? – It is when a gas ______________ energy and changes to a ____________________. • Think of examples in your life other than the cold drink in the summer that shows condensation. Yes, More Questions! • What is condensation? – It is when a gas ______ energy and changes to a __________. • Think of examples in your life other than the cold drink in the summer that shows condensation. • Steamy bathroom after a hot shower – “fog” on mirror! Phase Change Graph Sublimation – Solid to Gas • Solid to gas phase change occurs when a substance gains so much energy it is able to go directly from a solid to a gas, omitting the liquid phase! Sublimation: Solid to Gas • Ice will sublimate in your freezer! The molecules on the surface of the ice will gain enough energy to turn into a gas. • You may notice this in the cold winter with snow. The snow does not melt, but slowly disappears. Deposition: Gas to Solid • When water vapor in air loses so much energy it turns directly into a solid. • Frost! Questions – Just a couple… • Sublimation occurs when a substance __________ energy and goes directly from a _____________ to a __________. • Deposition occurs when a substance __________ energy and goes directly from a _____________ to a __________. Questions – Just a couple… • Sublimation occurs when a substance __gains energy and goes directly from a _solid to a _gas. • Deposition occurs when a substance _loses energy and goes directly from a gas_ to a solid. Energy in Phase Change DEPOSITION Deposition: Gas to Solid • When water vapor in air loses so much energy it turns directly into a solid. • Frost! Add the correct terms to the diagram… Temperature Comparisons • Boiling Point of H2O 212 F 100 C • Melting Point of H2O 32 F 0 C • Freezing Point of H2O 32 F 0 C Your Assignment… • Grass Garden Teams - Pick a number • In numerical order choose from the following: melting freezing vaporization condensation sublimation deposition Your TASK Communicate to the rest of the class what your phase change is. You may make a poster, present a newscast, create a jingle, or produce a skit. See Assignment Sheet for details. Phase Change Graph Phase Change Graph