Physical vs. Chemical Changes & Properties Presentation
advertisement

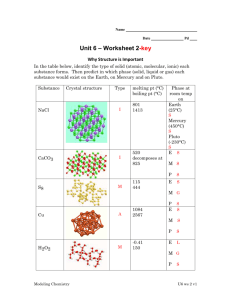
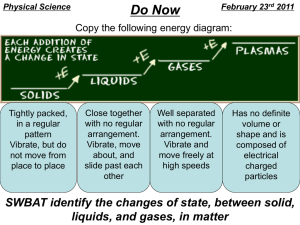
Physical vs Chemical Changes and Properties Properties – what are they? Property • The arrangement of atoms determines the properties of the substance • • • • • • • • • • • • Shape Color Texture Odor Luster Transparency Density Size Volume Mass Melting Point Boiling Point • • • • • • • • • • Mass Melting Point Boiling Point Freezing Point Hardness Resistance Flamable Conductivity Magnetism Insulator • Will every substance have all these properties? • Is the lack of a property a property? Physical Properties Physical Properties • Observations made about a substance that doesn’t change the substance itself • You can stretch a rubber band, bend a piece of wire, or break a piece of gum. • Because you are still left with the same substance when you are done, it is a physical property. Physical Properties • Appearance: • How would you describe a tennis ball? (shape, color, state of matter) • How would you describe a soft drink? (color, state of matter, taste) • You could also measure its volume and temperature—these are all physical properties Physical Properties • Behavior: • Some physical properties describe the behavior of a substance • For instance, objects containing iron (I.e. safety pins) are attracted by a magnet • Think about a soft drink. If you were to knock it over, it would spread onto the table and floor—the ability to flow is a physical property of liquids Physical Changes Physical Change • A physical change is a change in which a substance changes its physical properties without changing its chemical identity. • These changes might involve energy changes, but the kind of substance— the identity of the element or compound—does not change! Physical Change • Heat Curve Physical Change Physical Changes • KEYWORDS: – Freezing – Melting – Boiling – Condensing – Vaporizing – Evaporating – Change in size or shape – Dissolving Chemical Properties Chemical Properties • The chemical characteristics of a substance that tend to change the chemical identity. • A chemical property of Fe (Iron) is rusting. • Limestone and acid gives off gas in the form of bubbles –good indication that there is a chemical change occurring. Chemical Changes Chemical Change • The change of a substance into other substances through a reorganization of atoms. • Chemical reactions involve chemical changes. Chemical Changes • KEYWORD: – New substance formed? – Burning – Change in color – Gas given off (bubbles) – Precipitate (solid that falls out of solution) – Change in odor – Rusting Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions • Bonds between atoms are formed or broken causing substances to combine and recombine as different molecules. • Represented by chemical equations • Metabolism – all of the chemical rxns that occur within an organism Chemical Reactions YIELDS 2H2 + O2 Reactants 2 H2O Products • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, just rearranged! • The Chemical Equation must be balanced!! elements www.animationfactory.com