Ch - westscidept
advertisement

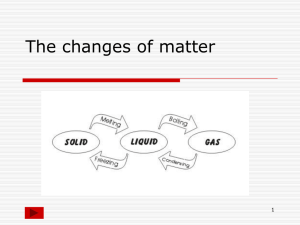
Ch. 4 Vocabulary – States of Matter (p. 123, 11 terms + 7) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. States of Matter Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Change of State Melting Evaporation Boiling Condensation Sublimation Atom Molecule Melting Point Freezing Freezing Point Boiling Point Condensation Point Unit 2 (Ch.4) - Structure of Matter Bach 10/05/09 Ch. 4 Vocabulary – States of Matter (p. 123, 11 terms + 7) 1. States of Matter The physical forms of matter, which include solid, liquid, and gas. 2. Solid The state of matter in which the volume and shape of a substance are fixed. 3. Liquid The state of matter that has a definite volume but not a definite shape. 4. Gas A form of matter that does not have a definite volume or shape. 5. Plasma In physical science, a state of matter that starts as a gas and then becomes ionized; it consists of free-moving ions and electrons, it takes on an electric charge, and its properties differ from the properties of a solid, liquid, or gas. 6. Change of State The change of a substance from one physical state to another. 7. Melting The change of state in which a solid becomes a liquid by adding heat. 8. Evaporation The change of state from a liquid to a gas. 9. Boiling The conversion of a liquid to a vapor when the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. 10. Condensation The change of state from a gas to a liquid. 11. Sublimation Unit 2 (Ch.4) - Structure of Matter Bach 10/05/09 The process in which a solid changes directly into a gas. 12.Atom The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. 13.Molecule A group of atoms that are held together by chemical forces; a molecule is the smallest unit of matter that can exist by itself and retain all of a substance’s chemical properties. 14.Melting Point The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. (A physical property/ characteristic property used to identify substances – melting point of water = 0°C). 15.Freezing The change of state from a liquid to a solid. 16.Freezing Point The temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid. (A physical property/ characteristic property used to identify substances – freezing point of water = 0°C). 17.Boiling Point The temperature at which a liquid changes into a vapor, or gas. (A physical property/ characteristic property used to identify substances – boiling point of water = 100°C). 18.Condensation Point The temperature at which a gas becomes a liquid. (A physical property/ characteristic property used to identify substances – condensation point of water = 100°C). Grading Scale (1 point per term) A = 18 - 17 B = 16 - 15 C = 14 - 13 Unit 2 (Ch.4) - Structure of Matter Bach 10/05/09 D = 12 - 11 F = 10 or less Unit 2 (Ch.4) - Structure of Matter Bach 10/05/09