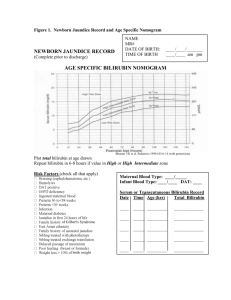
NEONATAL JAUNDICE DEFINITIONS Kernicterus | bilirubin encephalopathy; deposition of unconjugated bilirubin in the brain (especially basal ganglia and brainstem) causing encephalopathy Classical Presentation | lethargy/decreased LoC + poor feeding + hypotonia + jaundice FEATURES: HEPATIC DYSFUNCTION Jaundice Epistaxis Encephalopathy CAUSES OF JAUNDICE Hypotonia < 24h Old > 24h Old Persistent Peripheral Neuropathy Sepsis Sepsis Hypothyroidism Rickets (vit D deficiency) TORCH HDN G6PD, HS Physiologic Biliary Atresia Breastfeeding α1-Antitrypsin Deficiency Breast Milk Galactosemia Crigler-Najjar CF MANAGEMENT ABC Phototherapy Exchange Transfusion IVIG Other • Secure ABCs • Large bore IV cannulation • Senior help • Monitor Temperature • IV Fluid Management + Urine Output • Daily Weights • Eye Protection • 6hrly bilirubin monitoring • Significant unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia • HDN • Severe Anemia • Adjunct to phototherapy in HDN or rapidly ↑ bilirubin • Encourage breastfeeding • Do not give additional fluids if breastfeeding • Encourage cuddling and bonding with parents Therapy can be stopped once bilirubin < 50µmol/L below threshold Easy Brusing Petechiae Malnutrition Pruritis NEWBORN SCREENING (8 DISORDERS) Cystic Fibrosis Congenital Hypothyroidism Phenylketonuria (PKU) Galactosemia Glutaric Aciduria Type 1 (GA1) MCADD Homocysteinuria (HCU) Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) Investigations Blood • FBC + PBS (anemia, infection) • Bilirubin (incl direct & indirect) • LFT • TFT (hypothyroidism) • ABO Rh (HDN) • DAT (Coombs) Radiological Underlying cause of hyperbilirubinaemia and jaundice must be treated in order to definitely resolve neonatal jaundice. • Abdominal U/S Other • Newborn Blood Spot Screen • ± TBIDA scan ± Liver Bx