JAUNDICE
advertisement

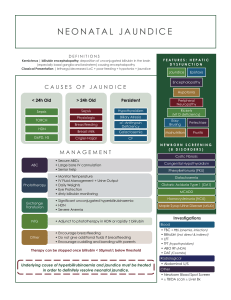
JAUNDICE By Anfal Gadour Objectives • Definition of Jaundice • Bilirubin Metabolism • Investigations • Categories • Common causes and management What do you already know? How would you define jaundice? What is the difference between conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin? How would you class the different causes of jaundice? What would you ask about in the history? What would you look for on examination? What is corvorsiers law? What are the most important investigations? Jaundice (icterus) Definition: Yellow discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes Due to increased Bilirubin concentration in the body Detectable when plasma levels are greater than 50 micromol/l (normal 3-17) Bilirubin Metabolism Haemoglobin GLOBIN FE 2+ LIVER BILE SI Investigations • LFTS: Bilirubin, ALP, AST, ALT, GGT USS abdo: GB, Cystic Duct, mass ERCP/MRCP: Stone, Biliary system Categories Prehepatic Hepatic Posthepatic Prehepatic Due to Haemolysis causing increased bilirubin production Decreased uptake by liver Decreased conjugation unconjugated bilirubin builds up in blood Water insoluble – therefore doesn’t enter urine Causes: Physiological (neonates), haemolysis, Gilberts syndrome Hepatic/Hepatocellular Hepatocyte Damage Causes: hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, liver metastases, rarer: haemochromatosis, AIH Posthepatic Obstructive jaundice Common bile duct is blocked Bilirubin overspills into blood – build up of conjugated bilirubin Water soluble – excreted in urine – dark Less conjugated bilirubin can reach the bowel – pale stools If severe – pruritus Causes: common bile duct stones, pancreatic cancer Gallstones Present in 10-20% of population Cholesterol and mixed Usually asymptomatic Risk factors: 4F’s Complications.. Biliary colic Pain associated with temporary obstruction of cystic or CBD by a stone Severe constant pain, subsides over several hours Pain radiates to right shoulder. Vomiting Examination normal Diagnosis: hx, raised ALP and bilirubin. ABSENCE OF INFLAMMATORY FEATURES. Manage: analgesia, elective cholecystectomy Acute Cholecystitis Stone in cystic duct or GB neck Hx similar to biliary colic. However, progresses to constant severe pain in RUQ Fever, tenderness and guarding Murphys sign INFLAMMATORY FEATURES – rasied WCC, fever, deranged LFTS, USS Manage conservatively: NBM, IV fluids, Analgesia, IV abx Cholecystectomy Ascending Cholangitis Infection on biliary tree Charcots triad – RUQ pain, Fever, Jaundice Dark urine, pale stools, pruritus Inv: raised WCC, Blood cultures, Deranged LFTS, USS, CT, ERCP Manage: Fluid resus, Analgesia, IV abx, ERCP Pancreatic cancer • Painless Jaundice • Older • Pale stools, dark urine • Weight loss • Palpable GB? • Usually head of the pancreas • Diagnosed on CT • Poor prognosis Any Questions?