Jaundice, final - Copy - mcstmf
advertisement
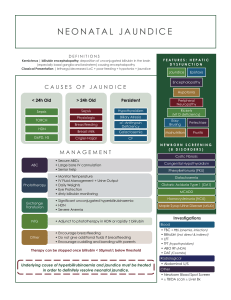
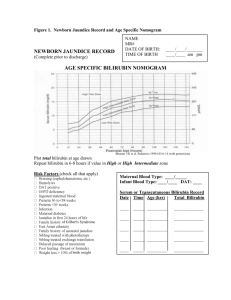
Jaundice Dr.Abdulaziz Alsoumali Intern Alyamamh hospital Pediatric rotation Content • • • • • • • Definition of jaundice Background & Epidemiology Bilirubin metabolism Classifications of jaundice Causes of neonatal jaundice Diagnosis Treatment Jaundice Definition: Definition • Yellow discoloration of : - The skin - The conjunctival membrane (sclera) • Jaundice is not a disease • Bilirubin Background & Epidemiology - Over 50% of all newborn infants become visibly jaundiced. - About 80% of pre-term newborn infants become jaundiced. - The red cell half life span of newborn infants is (70 days) - Hepatic bilirubin metabolism is less efficient in the first few days of life. Bilirubin metabolism Classification A) Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Hemolysis & Recticuloycytosis (+) Coombs test ABO & Rh incompatibility Autoimmune SLE Idiopathic acquired hemolytic anemia - Coombs test RBC enzyme defect (G6PD) RBC membrane defect (spherocytosis) No Hemolysis Gilbert syndrome Physiologic jaundice Breast milk jaundice Breast feeding Crigler-Najjar syndrome Hypothyrodisim Pyloric stenosis Classification B) Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Obstructive Biliary atresia Choledochal cyst Cholelithiasis Bile duct stenosis Tumor/neoplasia Spontanoeus bile duct perforation Bile-mucus plug Infectious Metabolic Hepatitis Cytomegalovirus Herpes simplex 1,2,6 Epstein-Barr virus Measles Varicella Bacterial sepsis Cholecystitis Wilson disease Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Galactosemia Cystic fibrosis Dubin-Johnson Rotor syndrome Classification B) Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Idiopathic e.g. Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis Autoimmune e.g. Autoimmune chronic hepatitis Sclerosing cholangitis Causes of neonatal jaundice Diagnosis (Clinical Assessment) • Jaundice appears clinically --> the bilirubin level reaches about 80 μmol/L Complications • Permanent damage --> Kernicterus - Athetoid cerebral palsy - developmental delay - hearing deficit - dental dysplasia - Permanent upward gaze (Parinaud’s sign) Complications • Reversible damage --> Acute bilirubin encephalopathy • Initial signs include: - lethargy - hypotonia - poor suck, progressing to - hypertonia (opisthotonos&retrocollis) - High pitched cry Treatment • Phototherapy Complications: Loose stools Erythematous macular rash Overheating --> leading to dehydration Bronze baby syndrome • Exchange transfusion - no response with phototherapy - reaches the threshold of the transfusion Take home message Literatures • Up to date • Tom Lissauer, Graham Clayden. Illustrated textbook of Pediatrics, 4th edition • NELSON, Essentials of pediatrics • Queensland Maternity and Neonatal Clinical guideline • NICE guidelines for neonatal jaundice Questions !!