IONS IN SOLUTION TAKS QUESTIONS
advertisement
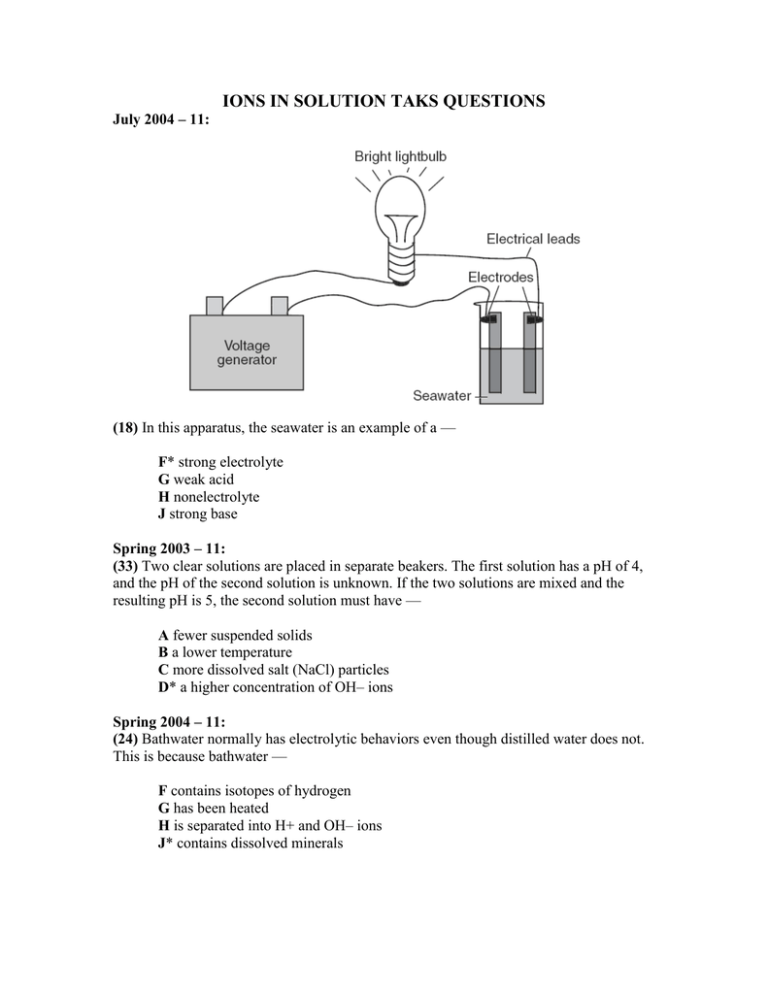
IONS IN SOLUTION TAKS QUESTIONS July 2004 – 11: (18) In this apparatus, the seawater is an example of a — F* strong electrolyte G weak acid H nonelectrolyte J strong base Spring 2003 – 11: (33) Two clear solutions are placed in separate beakers. The first solution has a pH of 4, and the pH of the second solution is unknown. If the two solutions are mixed and the resulting pH is 5, the second solution must have — A fewer suspended solids B a lower temperature C more dissolved salt (NaCl) particles D* a higher concentration of OH– ions Spring 2004 – 11: (24) Bathwater normally has electrolytic behaviors even though distilled water does not. This is because bathwater — F contains isotopes of hydrogen G has been heated H is separated into H+ and OH– ions J* contains dissolved minerals October 2005 – 11, July 2006 - 11: 37 The table shows data from an investigation designed to find a liquid solution that is both an acid and a strong electrolyte. Based on the data, a solution that is both an acid and a strong electrolyte is — A Solution 1 B Solution 2 C Solution 3 D* Solution 4 Fall 2005 – 11: 22 Dissolving salt in water increases the conductivity of the solution because the — F salt gives the solution a net negative charge G salt ions bond with the available water molecules H solution has an increase in kinetic energy J* concentration of ions in the solution increases