What does it mean to be an electrolyte? An electrolyte is a
advertisement
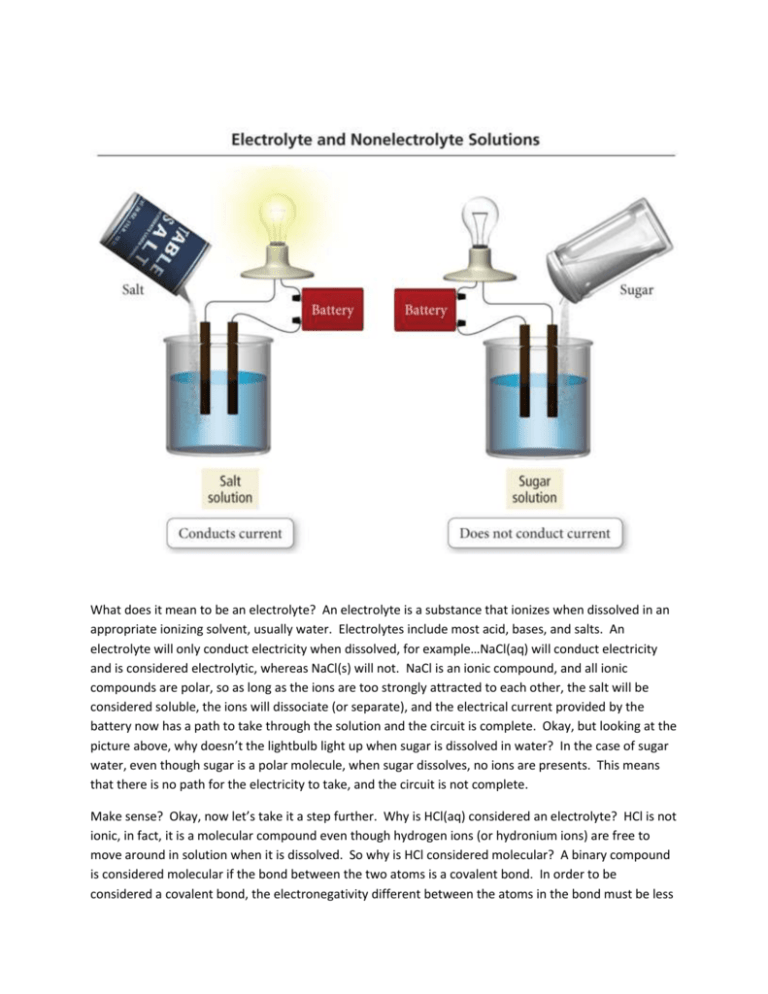
What does it mean to be an electrolyte? An electrolyte is a substance that ionizes when dissolved in an appropriate ionizing solvent, usually water. Electrolytes include most acid, bases, and salts. An electrolyte will only conduct electricity when dissolved, for example…NaCl(aq) will conduct electricity and is considered electrolytic, whereas NaCl(s) will not. NaCl is an ionic compound, and all ionic compounds are polar, so as long as the ions are too strongly attracted to each other, the salt will be considered soluble, the ions will dissociate (or separate), and the electrical current provided by the battery now has a path to take through the solution and the circuit is complete. Okay, but looking at the picture above, why doesn’t the lightbulb light up when sugar is dissolved in water? In the case of sugar water, even though sugar is a polar molecule, when sugar dissolves, no ions are presents. This means that there is no path for the electricity to take, and the circuit is not complete. Make sense? Okay, now let’s take it a step further. Why is HCl(aq) considered an electrolyte? HCl is not ionic, in fact, it is a molecular compound even though hydrogen ions (or hydronium ions) are free to move around in solution when it is dissolved. So why is HCl considered molecular? A binary compound is considered molecular if the bond between the two atoms is a covalent bond. In order to be considered a covalent bond, the electronegativity different between the atoms in the bond must be less than 2 and no metal can be present. The electronegativity difference between atoms determines how polar the bond between those two atoms is.