Chapter 19 Manufacturing Accounts
advertisement

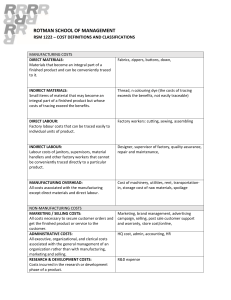
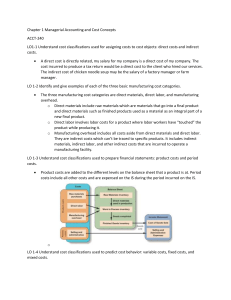
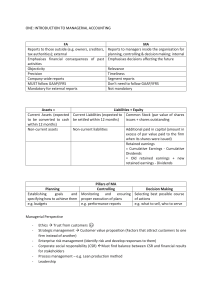
Chapter 19 Manufacturing Accounts Manufacturing Companies • A Manufacturing Firm is one which converts raw materials into finished goods and sells the finished goods to make a profit. • A Manufacturing Account is prepared to calculate the cost of producing completed goods. Direct vs Indirect Cost DIRECT COST INDIRECT COST 1. Direct materials or raw materials – these are materials used or consumed in production. 1. Indirect materials – these costs are essential in a firm’s operations but cannot directly be traced in the production of goods. 2. Direct labour or production 2. Indirect labour – these are cost labour – these are cost incurred incurred paid as wages to paid as wages to people who people who support in the work directly on the product. development of a product however, the cost of the labour cannot be traced to the actual product for example: foreman wages. SECTIONS OF A MANUFACTURING ACCOUNT • Prime cost – contains the direct (variable) cost related to the volume of production. • Factory overheads – contains cost that are likely to be incurred regardless to the number of units produced. • Work-In-Progress – contains opening and closing stock of semi-finished goods. The Trading Account The components of the trading account would include: • Cost of goods manufactured transferred from the manufacturing account. • Opening stock and closing stock of finished goods. • Sales of finished goods. • Purchases of finished if the manufacturing company buys from another supplier. The Profit & Loss Account The components of the profit and loss account would include costs not related to the making of the product: • Administrative (office) expenses • Selling and distribution expenses • Financial expenses. The Balance Sheet The Balance Sheet differs from other businesses because of the three types of stock. These types of stocks(raw materials, work in progress and finished goods) are shown separately in the Current Assets section in the Balance sheet.