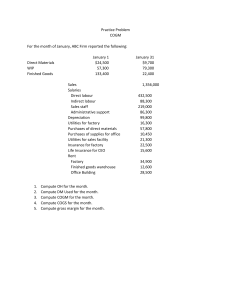
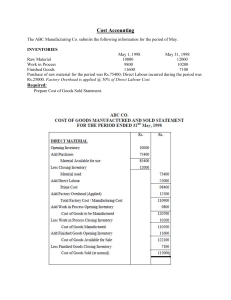
Topic 1 Introduction to Cost Accounting Topic 1-Learning Objectives On completing this topic, candidates ought to:1.Define Cost Accounting and differentiate if from Management Accounting 2. Contrast Cost and Financial Accounting 3. Define Cost Terms 4. Identify the 3 main cost components 5. Draw up the COGM and COGS 6. Trace the flow of cost from purchase of RM to sales of completed goods Definition of Cost Accounting • Cost Accounting (CA) accounts for costs • It accumulates & assigns historical costs to units, products, services in order to determine an Income. • CA leads on to Management Accounting which provides relevant information to assist management to plan (budget) and control/monitor their operations to achieve organizational goals. • CA serves internal users. It determines costs for pricing and minimizes costs thru planning for a higher profit. CA also provides tools for decision Accounting Tools for Decisions • Two main Accounting tools are: 1. Budgets which are Elements of control 2. Performance report which provides the feed back. Differences (variances) are noted from reports and are rectified or corrected to achieve the entity’s objectives. These tools are cyclic: Plan-implement-monitor-report-appraiseadjust further plan Cycle of Planning Role of Cost Accounting • CA accumulates costs and informs management. • Accounting System is: 1. to provide timely information 1. to interested parties 2. to make informed decisions. • Accounting is an economic commodity with costs, so it must generate benefits. Accounts for Changes • Accounts provide the feed back. Feedback may be used to: - change method of appraisal or rewarding system -search for alternative source or method -change method of operation/approach -make projections or predict future - change goals/objectives for the better Cost Acct versus Financial Acct • Financial Accounting -Legally Required for outside users -Guided by GAAP:A=L+P -Historical value/inform. expressed in Kina/toea -annually, can be qtrly, mthly -Subject to lawsuit -One report for the whole entity • Cost Accounting -Optional for internal users -Report varies with use -Historical information expressed in kina/toea -Report period varies with purpose: wkly, mthly -no legal liability -Responsibility centers provide report Cost Terms • Cost Object- any activity/item that requires a cost measure • Costing-accumulation of cost data to compute a price • Fixed Costs-costs which do not change with activity within a range (certain time & range of activity) • Variable costs-those which vary with activity Cost terms cont • Average Cost-total cost divided by some denominator (eg. units produced)=unit cost • Manufacturing costs-costs of transforming raw materials into finished goods • Non Manufacturing costs are those not directly related to production Cost terms Cont. • Direct Costs-costs of raw material & labor input into production-Prime Cost • Indirect costs-costs other than Prime Costs, often referred to as factory burden or overhead • Conversion Costs-cost of labor & overhead Elements of Manufacturing Costs 1. Direct Materials- all physically observable material input of a product 2. Direct Labour-all physically observable labour input of a product [1+2=Prime Cost] 3. Overhead-indirect man. costs-costs other than 1 & 2. OH can be fixed (insurance, rent rate etc) or variable (power, supplies, janitorial/foreman) [2+3=Conversion Cost] Product costs • Product costs (Inventoried) are costs identified with goods made/purchased & expensed as COGS. Sales-COGS=Gross Profit Gross Profit-Operating costs=Net Profit • Period Costs are non product costs expensed during that current period. Flow of costs • Raw Material Purchase Stores • Labour Work in Progress • Overhead Finished goods Sales Debtors Cash Review of Double Entry • It is assumed that candidates have the basics of double. This was covered in the Introductory class • Rest of Journal Entries in this course build up on the above assumption • The onus is on you to review the Double Entries if it is shallow or rusty Accounting for costs • Every arrow in the flow diagram above represents an Accounting Entry. • Example: Arrow above Raw Materials represents raw materials purchased. Accounting Entry is: • Dr Raw materials xx • Cr Cash(Bank)/Accounts Payable xx End Product of CA • End product of keeping account is to produce: • a. Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) • b. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) • These two statements will enable an entity to determine the operating result (Profit/Loss) • Below are some examples for illustration: Cost Ledger Accounts • Only CA are extracted to illustrate COGM & COGS from the General ledger • Study and first illustration and attempt the next one as a re-enforcement exercise before you come to the next • Both are presented in a Statement Format making them easier for laymen. Whilst COGM & COGS are done separately, they can be combined Cost Of Goods Manufactured /COGS The following data pertains to Henderson Parts Company • From the following data, prepare a COGM & COGS statements: 1.1.x08 31.12.x08 Inventories: Finished Gds K16200 K33620 Raw Materials 8000 7300 Work in Process 6200 5100 Direct Labour 64500 Freight In 1612 Indirect Labour 24020 Indirect Material used 1819 Insurance 2837 Depreciation of Plant & Equipment 3501 Raw Materials (Direct) purchased 130000 Payroll Tax Expense 5617 Power & Light 4725 Property Taxes 5220 Raw Materials Returns & Allowance 310 Repairs & Maintenance 3016 Henderson Parts Company Statement of COGM for period ending31.12.x08 Work in Process (1.1.x08) Add Raw Materials used: Raw Materials (1.1.x08) +Raw Mat purchased 130000 +Freight In 1612 131612 -Purchase Rets 310 Total Raw Materials Less Raw Materials 31.12.x08 Raw Materials Used Add Direct Labour ** Prime Cost is K6200 8000 131302 139302 7300 132002 64500 196502 Add Factory Overhead: Indirect Labour 24020 Indirect Mat Used 1819 Depreciation 3501 Insurance 2937 Payroll Tax Exp 5617 Power and Light 4725 Property Taxes 5220 Repair & Maint. 3016 Total Costs Less Work in Process (31.12.x08) Cost of Goods Manufactured: 50855 253557 5100 248457 Cost of Goods Sold Henderson Parts Company Statement of COGS for period ending 31.12.x08 Finished Goods 1/1/x08 K 16200 Add Cost Of Goods Manufactured 248457 Total goods for sale 264657 Less Finished Goods 31/12/x08 33620 Cost of Goods Sold: 231037 Next Exercise for Reenforcement • You are advised to revise the above exercise by studying the COGM & COGS, statements. Then attempt the next exercise; before checking the solution that follow Cost Of Goods Manufactured /COGS The following data pertains to Power Furniture Limited • From the following data, prepare a COGM & COGS statements: 1.1.x4 31.12.x4 Inventories:Finished Gds K618000 K531000 Raw Materials 304500 368200 Work in Process 103000 88750 Direct Labour 1444000 Freight In 33940 Indirect Labour 416500 Indirect Material used 67340 Insurance 18550 Depreciation of Plant & Equipment 116800 Raw Materials (Direct) purchased 2040000 Payroll Tax Expense Power & Light Property Taxes Raw Materials Returns & Allow Repairs & Maintenance Patent Amortization Waste Removal 115600 83010 42700 2720 61400 1600 6800 Power Furniture Limited Statement of COGM for period ending31.12.x4 Work in Process (1.1.x4) K103000 Add Raw Materials used: Raw Materials (1.1.x4) 304500 +Raw Mat purchased 2040000 +Freight In 33940 2073940 -Purchase Rets 2720 2071220 Total Raw Materials 2375720 Less Raw Materials 31.12.x1 368200 Raw Materials Used 2007520 Add Direct Labour 1444000 COGM cont. Add Factory Overhead: Indirect Labour 416500 Indirect Mat Used 67340 Depreciation 116800 Insurance 18550 Payroll Tax Exp 115600 Power and Light 83010 Property Taxes 42700 Repair & Maint. 61400 Patent Amortisation 1600 Waste Removal 6800 Total Costs Less Work in Process (31.12.x1) Cost of Goods Manufactured: 930300 4484820 88750 4396070 Cost of Goods Sold Power Furniture Limited Statement of COGS for period ending 31.12.x1 Finished Goods 1/1/x1 K 618000 Add Cost Of Goods Manufactured 4396070 Total goods for sale 5014070 Less Finished Goods 31/12/x1 531000 Cost of Goods Sold: 4483070 Major Components of any Cost Object • Three cost components are combined to get COGM: Raw Material, Direct Labour and Overhead. • Each will be covered in topics 2-4 • Topic 5 will combine the three to calculate costs • SO BE SURE TO UNDERSTAND EACH ONE TO MAKE EASY FOR YOURSELF DURING TOPIC 5