Matter and Energy
advertisement

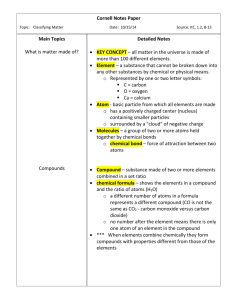
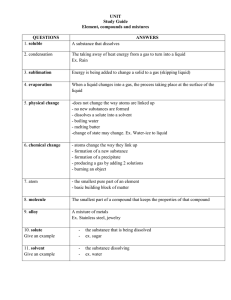
Matter and Energy Name _______________________________ Applied Chemistry Date: __________________ Period: ______ I. The UNIVERSE is made of _______________ and _______________. II. Energy A. Definition: Energy is the capacity to do ______________ or to produce _____________. 1. Common Unit: ___________________abbreviated ______________. 2. SI Unit: ________________ abbreviated _______________. B. Forms 1. Radiant Energy is energy transferred ______________________. Example: ________________ 2. Kinetic Energy is the energy of _________________. Examples: _________________ _________________ _________________ 3. Potential Energy is energy of _________________ or ______________________. Examples: _________________ _________________ C. Law of Conservation of Energy 1. Energy is neither ______________ nor ________________. 2. Energy can change from one ______________ to another. III. Matter A. Definition: Matter is anything that has ______________ and _____________. B. States of Matter 1. Identification Table NAME ABBREV SHAPE VOLUME DENSITY 2. Change in state is also known as a _____________________________. (See next page for changes between states.) 1 2 C. Properties or Characteristics of Matter 1. A physical property is a property _____________________ or __________________ without changing the material. Examples: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 2. A chemical property is a property that refers to the ability of a material to undergo a ________________ that alters its structure. Examples: _________________________ _________________________ D. Changes 1. All changes involve a change in _________________. 2. Physical Changes: Do NOT change the __________________ of a substance. Examples: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 3. Chemical Changes: ________________ the identity of a substance. Examples: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 4. Signs of a Chemical Change: _________________________________, ________________________________, _________________________________, ________________________________, or _________________________________. a. Chemical Equation – a shorthand way to write a ________________ _____________. Starting materials are called ____________________. Newly formed materials are called ___________________. Reactants Products Yield Iron + Oxygen Rust (Iron(II) oxide) E. Law of Conservation of Matter 1. Matter is neither __________________ nor ___________________. It only changes _____________________. 2. Shown by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier in the 1700s. He is known as the Father of _________________. mass of the ____________________ = mass of the ____________________ 3 F. Classification of Matter 1. Pure substances a. Elements Contain only ______________________________. _______________ be broken down by ordinary methods. (chemical/physical) Ancient Greeks believed in only _______ elements (________________, _________________, ________________, _________________) _____ naturally occurring elements. Others are short-lived, man-made elements. A _____________________ is a shorthand way of writing the name of an element. Represents 1 _______________ of an element. 1. 2. 3. 4. Consists of 1 or 2 letters 1st letter is ALWAYS capitalized. Subsequent letter is lower case. 3-letter symbols are temporary designations assigned by IUPAC. Ex. Hydrogen _______ Helium Carbon _______ ________ Chlorine ________ # of elements as a Solid, Liquid, or Gas at room temperature ___________ Liquids ___________ Gases All others are solids. b. Compounds Contain _______________________________________ that are chemically combined. Can be broken down by chemical processes, such as ________________________. Smallest particle of a compound is a A __________________ is a shorthand way of writing the name of a compound. It . shows: 1. Which elements are present 2. The ratio of the elements present. Example: H2O - the 2 is called a __________________ that tells you that ______________of hydrogen combine with ____________ of oxygen to form _______________________ of water. Example: 3 H2O is read as 3 _________________ of water. The 3 is called a __________________. There are ________ hydrogen atoms and ________ oxygen atoms. 4 Element or Compound? Co _______________ CO _____________ CS _______________ Mg ______________ How many atoms are in Na2SO4? ___________ How many atoms are in Ca(OH)2? ___________ How many atoms are in 3Fe2(SO3)3? ___________ 2. Mixtures contain _______________________________ that are mixed together but _________________ chemically joined. A. Homogeneous Mixture or Solution ____________________ throughout Not visibly different Examples: _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ ______________________ B. Heterogeneous Mixture or Mechanical Mixture Not ____________________ throughout Visibly different (layers) Examples: _____________________ ______________________ _____________________ ______________________ 5 IV. Separation Techniques A. Heterogeneous Mixtures 1. Filtration Separate _____________________ from a clear liquid by pouring through a __________________, __________________, or __________________. filtrate: residue: Examples: _____________________ ______________________ 2. Magnetic Method Separate _________________ substances from _________________ substances. Examples: ______________________ _____________________ 3. Decanting Separate _____________________ due to a difference in _____________. Example: _______________________ B. Homogenous Mixtures: 1. Chromatography Separate ________________ of ink using strips of paper. Examples: ______________________ ______________________ 2. Distillation Separate solution by a difference in ______________________. The liquids will evaporate and then _________________ back to a liquid. Example: _____________________ 3. Crystallization Separate a solution by __________________ the liquid and the solid will __________. Examples: _______________________ _________________________ 6