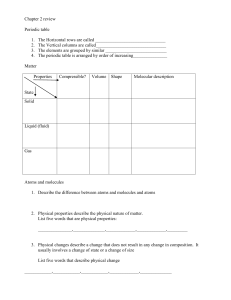
Lower Secondary 7 Science Checkpoint Essential Question: How are elements, compounds, and mixtures related? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume) There are different types of Matter: Pure Substances (elements and compounds) and Mixtures The composition (structure) of a substance determines its Matter type. Characteristics of Pure Substances • Fixed composition • Distinct properties • Cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods • Can only be changed in identity and properties by chemical methods • Properties do not vary one sample to another sample How many different substances are there? How many different substances can you think of? There are millions of different substances! What are they all made of? All substances are made of atoms All substances are made of very tiny particles called atoms. Many substances are made up of different types of atoms. hydrogen and oxygen atoms carbon and hydrogen atoms iron, aluminium, silicon, oxygen and boron atoms carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and sulphur atoms Types of Pure Substances: Elements And Compounds What is an element? All substances are made of very tiny particles called atoms. There are about one hundred substances that are made up of just one type of atom. These are the elements. carbon helium copper The elements are the simplest substances in the universe. The elements are the building blocks of all other substances. Elements • Made up of one type of atom • Cannot be broken down by physical and chemical methods • Examples: Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon Sample of the Element Lead Sample of the Element Chlorine Atoms in elements An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. Copper is an element made up of copper atoms only. Carbon is an element made up of carbon atoms only. Helium is an element made up of helium atoms only. Atoms and molecules of elements An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. In some elements, the atoms are joined in groups of two or more. A particle containing atoms grouped in this way is called a molecule. Oxygen is an element made up of oxygen atoms only. How many atoms are there in an oxygen molecule? Other elements, that contain atoms joined in molecules are hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and bromine. Introducing chemical symbols A standard set of symbols is used to represent elements: The symbol for many of the more common elements uses just the first letter of the name. H = hydrogen C = carbon F = fluorine Others elements have the first two letters. Ca = calcium Al = aluminium He = helium O = oxygen N = nitrogen I = iodine Some of the symbols are not always as you might expect. Mg = magnesium Au = gold Ag = silver How to write symbols for elements Two important rules should be followed when writing the symbols of elements so that there is no confusion. 1. The first letter of an element’s symbol is always a capital letter. e.g. N (not n) for nitrogen 2. If there are two letters in the element’s symbol, the second letter is always a small letter. e.g. Co (not CO) for cobalt No, Watson! It was carbon monoxide poisoning – not cobalt. The Periodic Table • • • • arranging the elements It is organized in rows and columns The rows are called periods The columns are called groups Group Period METALS • are very useful materials • are the substances from which objects are made Properties of Metals • are usually shiny when polished or freshly cut • ring like a bell when you hit them • strong and tough, they do not shatter when dropped and they do not cracks easily • can be shaped by bending them. They are malleable, which means that they can be hammered into shape. They are ductile, which means that they can be drawn out into wires. Properties of Metals • don’t melt easily • Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature • Are magnetic: like iron, steel, nickel, and cobalt • Are good conductors of heat. When you touch them they conduct heat energy away from the hand so they feel cold. Non-metals Comparing metals and non-metals Classification of Elements as Metals and Non- Metals No. METALS NON- METALS 1 Good conductors of electricity & heat Bad conductors of heat & electricity 2 Shiny in appearance Usually dull in appearance 3 Strong & hard Usually weak & soft 4 Malleable & ductile Brittle ELEMENTS & SYMBOLS NON-METALS METALS No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NAME SYMBOL PHYSICAL STATE NAME Aluminium Al Solid Argon Calcium Ca Solid Bromine Copper Cu Solid Carbon Iron Fe Solid Chlorine Magnesium Mg Solid Silicon Mercury Hg Liquid Sulphur Potassium K Solid Hydrogen Sodium Na Solid Iodine Zinc Zn Solid Nitrogen Solid Gold Au oxygen * Physical states are given at room temperature. SYMBOL PHYSICAL STATE Ar Br C Cl Si S H I N O Gas Liquid Solid Gas Solid Solid Gas Solid Gas Gas Alloys Stainless steel is a mixture of iron and chromium. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Metal or non-metal? Is this element a metal or a non-metal ? Hard to say! H He Li Be B C N O F Ne iron (Fe) antimony (Sb) iodine (I) copper (Cu) phosphorus (P) sulfur (S)(Mg) magnesium Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt ? ? ? Metals and non-metals in the periodic table The periodic table is a list of all the known elements which are arranged according to the similarities in their properties. Non-metals are Metals are on the mostly on the right. left and in the centre. Xe What type of elements are between metals and non-metals? Metal, non-metal or metalloid? francium krypton (Kr) (Fr) silicon(Co) (Si) scandium (Sc) cobalt Which side What are areare thethe nonmetalloids? metals on? H Li Be Na Mg K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Cs Ba La Fr Ra Ac Ti Zr Hf Rf metalloid non-metal metal He B C N O F Ne Al Si P S Cl Ar V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Db Sg Bh Hs Mt ? ? ? Metals are on Metalloids sometimes Non-metals the left and in behave like metals and are mostly the centre. sometimes like non-metals. on the right. Everyday materials and their properties Glass • Transparent • Waterproof • It can be recycled Plastic • Transparent or opaque • Used for containers for food and drink. It does not react with the food. • It is light in weight. • It can be recycled. What is a compound? A compound is the substance produced when two or more elements combine in a chemical reaction. Two elements, hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O), combine to make the compound, water. Which two elements combine to make the compound carbon dioxide? A compound is always made up of two or more different types of atom. Compounds • Form when two or more different elements join (bond) together chemically • Composition is identical in each sample • Can be separated only by chemical methods • Properties of a compound are totally different than the properties of the elements that form them • Examples: Water, Carbon dioxide, Sugar Animated images and notes from http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/atoms/elements.html Compounds Atoms in elements and compounds Elements are materials made up of one type of atom only. The element, hydrogen, exists as molecules. Each hydrogen molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms joined together. H H Compounds contain two or more different types of atom. The compound, water, exists as molecules. Each water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms joined to one oxygen atom. Making a compound – water A compound is made when atoms of different elements react and join together. For example, water is produced from the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. hydrogen + oxygen water H H + O O H H Two hydrogen molecules react with one oxygen molecule to produce two molecules of water. Why does water have different properties to its elements? Making a compound – carbon dioxide A compound has very different properties to the elements from which it is made. elements carbon oxygen combines with A black solid which can be used as a fuel. C compound carbon dioxide to make A colourless gas which is essential for life. + O O A colourless gas which is used to put out fires. Making a compound – water What are the elements which make up water? In what ways are the elements different to their compound? elements compound oxygen hydrogen combines with A colourless gas which is used in hot air balloons. water to make A colourless gas which is essential for life. A liquid which is essential to our lives and has many different uses. A compound is not a mixture The atoms in a mixture of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas, which have not reacted with each other, look like this… The atoms in water, the compound made when hydrogen and oxygen react and their atoms become chemically joined to each other, look like this… What is a mixture? A mixture contains two or more substances that are mixed together but have not reacted with each other. Sea water is a mixture of salts, water and other substances. A mixture is not the same as a compound: 1. The proportions of the substances in a mixture are not fixed. 2. The properties of a mixture are often an “average” of the properties of its ingredients (e.g. a mixture of a black and white powder is grey). 3. The substances in a mixture are just mixed, not chemically joined, and so it is usually quite easy to separate the ingredients (e.g. it is easy to get salt from sea water). Mixtures • Form when elements and/or compounds are combined physically • Properties of a mixture are related to its components • Composition varies from sample to sample • Can be separated by physical methods • Examples of Mixtures: Tea, Perfume, Air, Salad, Beach sand, oil and vinegar salad dressing, etc. Mixtures Mixture of Different Elements Mixture of Different Compounds Mixtures • A mixture of lead atoms and chlorine atoms. They exist in no particular ratio and are not chemically combined with each other. They can be separated by physical means. • A mixture of PbCl2 and PbCl4 formula units. Again, they are in no particular ratio to each other and can be separated without chemical change. Mixtures Mixtures are often referred to as homogeneous or heterogeneous. Mixtures • Homogeneous mixtures (Solutions) have a uniform distribution. • For example: Tea, Perfume, Air Mixtures • Heterogeneous mixtures do not have a uniform distribution. • Parts are often visible • For example: Salad, Beach Sand, Oil and Vinegar dressing Types of Mixtures There are THREE types of mixtures: Solutions Colloids Suspensions Solutions • A solution is a mixture that appears to be a single substance, but it is actually composed of 2 or more substances that are distributed evenly amongst each other. • A solution always has solute (a substance that is dissolved) and solvent (a substance that does the dissolving) ▫ SOLUTIONS ARE HOMOGENEOUS carbon dioxide is dissolved in water salt is dissolved in water sugar is dissolved in water Types of solutions Solute Solvent Example Gas Gas Gas Liquid Solid Liquid Air (oxygen in nitrogen) Soda water (carbon dioxide in water) Ocean water (salt in water) Solid Solid Gold jewelry (copper in gold) Metals dissolved in metals are called alloys. Colloids • A colloid is a mixture in which the particles are mixed together but not dissolved ▫ COLLOIDS ARE HOMOGENEOUS Colloids have properties of both solutions and . suspensions cloud mayonnaise milk Suspensions • A suspension is a mixture in which particles of a material are dispersed throughout a liquid or gas, but are large enough that they settle out. ▫ SUSPENSIONS ARE HETEROGENEOUS muddy water Italian dressing Distinguishing between Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Distributed Summarizing The diagram below shows how two elements can be mixed together…Which is a Compound? A Mixture? C. Compound A. B. D. Mixture Match the Picture to the Description Compound of 2 Elements Mixture of Molecules Element Molecule Compound of 3 Elements Element/ Atoms Mixture of Atoms Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Constructed Response Use the list of substances below to answer the following question. Summarizing Strategy: Elements, Compounds, & Mixtures Constructed Response Water Table salt (NaCl) Pure gold ring Pizza Air Carbon dioxide (dry ice) Nitrogen a. Categorize each substance as an element, a compound, or a mixture. b. Explain how each substance belongs in the category you chose. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________