UNIT Study Guide Element, compounds and mixtures QUESTIONS
advertisement

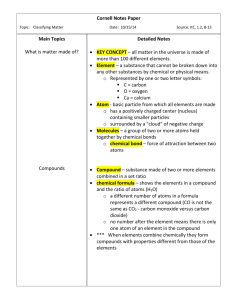
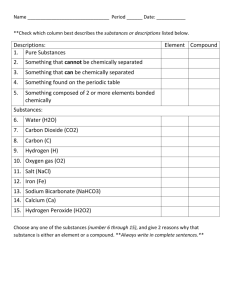
UNIT Study Guide Element, compounds and mixtures QUESTIONS 1. soluble ANSWERS A substance that dissolves 2. condensation The taking away of heat energy from a gas to turn into a liquid Ex. Rain 3. sublimation Energy is being added to change a solid to a gas (skipping liquid) 4. evaporation When a liquid changes into a gas, the process taking place at the surface of the liquid 5. physical change -does not change the way atoms are linked up - no new substances are formed - dissolves a solute into a solvent - boiling water - melting butter -change of state may change. Ex. Water-ice to liquid 6. chemical change - atoms change the way they link up - formation of a new substance - formation of a precipitate - producing a gas by adding 2 solutions - burning an object 7. atom - the smallest pure part of an element - basic building block of matter 8. molecule The smallest part of a compound that keeps the properties of that compound 9. alloy A mixture of metals Ex. Stainless steel, jewelry 10. solute Give an example - the substance that is being dissolved ex. sugar 11. solvent Give an example - the substance dissolving ex. water 12. element -made of one kind of atom -cannot be broken down into simpler substances 13. mixture - can be heterogeneous or homogenous mixture -consists of 2 or more substances that are mixed nut not chemically combined - ex. combination of sand, salt & water - ex. solution - ex. Sugar water 14. compound -Two or more elements chemically combined ex. H2O -Energy, such as electricity, is involved when it is taken apart -difficult to change back to the original substance - substances chemically combined -properties of substances are greatly different from properties of the substances from which it is made -specific amount of each substance must be used - a simplest compound has at least a metal & a nonmetal 15.How do you make or separate compounds -using electricity 16. formula -Can be written for every compound -Tells which elements are used and how many of the atoms there are in each element 17. subscript Represents the number of atoms of an element in a compound 18. fill in the following chart with correct information Solids Liquids Gases Definite volume? yes yes no Definite shape? yes no no Distance between molecules? Close together Medium spread Far apart 19. What is the smallest molecule part of a compound? 20. What is the smallest atom part of an element? 21. colloids Give 3 examples. Heterogeneous mixture where particles are permanently suspended and they are not dissolved. Do not settle and are not dissolved Ex. Fog, milk, whip cream, mayonnaise 22. Tell the difference between homogenous vs. heterogeneous mixtures .-heterogeneous (big particles) are least mixed (hard to separate) -homogenous (small particles) are very well mixed 23. Name the chemical and physical properties of sugar? Physical properties – white, grainy, sweet Chemical properties – dissolvable, flammable 24. List 4 differences between mixtures and a compound - mixtures can be separated physically - in a mixture the properties stay the same -a compound can be chemically separated -a compound has different properties then the elements making it up. Ex. Salt 25. How can water be broken down into its elements and what results? 26. What causes a glowing splint to relight? 27. What is the test to find out if a gas is oxygen? 28. Know how to figure out the names of the elements in a compound and the numbers of atoms of each element in that compound: EX. Ca3(PO4)2 29. Be able to name simple compounds and know what they are made of – a metal and a nonmetal. Ex: BaF2 30. Where are metals and nonmetals located on the periodic table? -using electricity - 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen oxygen If the glowing splint relights See pages 15, 21 & 22 in your notebook Name the first element and , change the ending to “ide” of the second element Metals on the left Non-metals on the right of the stairs starting with Boron on the periodic table The metal is written first, then followed by the non-metals 31. Tell two things about solutions -The solute never rises to the top or settles at the bottom - cannot be easily separated by physical means - the particles of a solution are evenly spread out - cannot be filtered 32. What type of energy is needed to change matter from one phase to another? - heat energy 33. chemical property - rusting - burning 34. physical property - melting 35. What are 3 differences between a physical and a chemical change? PHYSICAL -no new substances are formed -chemical properties stay the same -no energy is taken or given (unless phase change occurs) CHEMICAL -new substances form -new substance has different chemical properties from the original -energy is taken or given 36. What are 3 ways to recognize that a chemical change has taken place? - new substances formed -are atoms linked in the same way 34. tell 3 things about all solutions -cannot be easily separated by physical means -particles are evenly spread out -always has dissolved substance in it -cannot be filtered