SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 2 Learning Targets
advertisement

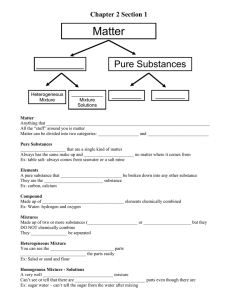
SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 2 Learning Targets Directions: Use the rating scale below to determine how well you know and can perform each of the learning targets below. Rating Scale: 0 What’s that? 1 I know a little bit 2 I know a lot # Learning Targets: 1 2 3 I am able to define matter and its properties. I am able to explain the difference between a physical and a chemical property of matter. I am able to use the density formula to calculate for mass, volume, or density using the appropriate units. 4 I am able to compare densities to determine the buoyancy of substances. 5 I am able to read chemical formulas and determine the number of atoms and elements in a molecule. 6 I can explain the difference between an atom and a molecule. 7 I am able to explain the difference between an element, compound, pure substance, and a mixture. 8 I am able to give examples of elements, compounds, and mixtures. I am able to determine if a mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous and give examples of each type. I am able to design a process and use it to separate a mixture into its separate 10 components. 9 11 I am able to determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. 12 I am able to explain the difference between physical and chemical changes. 13 I can give examples of physical and chemical changes. 3 I could teach this! Before After SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 2 Study Guide **Due on: _______________________** Directions: Complete each of the items below on a separate sheet of notebook paper. Be sure to number each item. 1. Define matter and density. 2. Why is density an important property of matter? 3. Use the density formula to solve for the missing property in the problems below. Be sure to include the appropriate units. a. Mass = _________ Volume = 85.2 mL Density = 1.2 g/mL b. Mass = 16.32 g Volume = _________ Density = 0.64 g/mL c. Mass = 500 g Volume = 375 mL Density = _________ 4. Identify if the objects above would sink or float in water. 5. Compare the densities of the substances below to determine in what order they would “stack up” in a graduated cylinder. a. Substance D: 0.03 g/mL d. Substance G: 0.33 g/mL b. Substance E: 0.3 g/mL e. Substance H: 0.93 g/mL c. Substance F: 1.03 g/mL f. Substance I: 1.30 g/mL 6. Identify the number of atoms, the number of elements, and the number of Hydrogen atoms in each of the chemical formulas listed below: a. C2H4 b. C6H12O6 c. C3H7OH 7/8. Explain the difference between: a. Atoms and molecules b. Compounds and elements c. Pure substances and mixtures d. Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures e. Physical and chemical properties f. Physical and chemical changes 9. What are the two categories that all pure substances would fit into? 10. Identify if the following substances are an element (E), compound (C), homogeneous mixture (HO) or heterogeneous mixture (HE) a. Sulfur (S) e. Aluminum (Al) b. Methane (CH4) f. Fruit salad c. Salt water g. Carbon Monoxide (CO) d. Milk h. Soil 11. Give two examples of a physical change 12. Give two examples of a chemical change