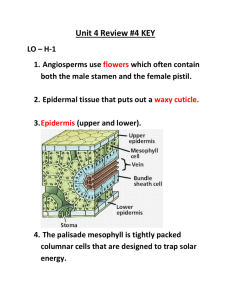
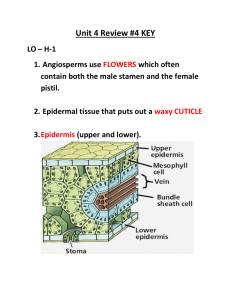
Plant Study Guide: Diversity, Structure, Reproduction
advertisement

Unit 7 Plants Study Guide Chapter 20 Plant Diversity 1. List four characteristics of plants. 2. What is thought to be the ancestor of plants? Name the genus. 3. Describe 2 characteristics of plants help them retain moisture. 4. What does the vascular system do? 5. What 2 adaptations aid plants in reproducing on land? 6. Draw a cladogram illustrating the evolution of these plant groups: mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms. 7. What classification term sometimes is used for plants instead of “phylum?” 8. What is a fruit? 9. Fill out the following chart on the classification of plants: Seedless nonvascular plants Seedless vascular Conifers plants Major Characteristics Which generation is dominant: sporophyte or gametophyte? How they reproduce Give 3 examples 10. Why is coevolution between flowering plants and animals important? 11. What is a cotyledon? 12. What is the difference between herbaceous and woody stems? Angiosperms 13. Fill out the following table regarding monocots and dicots: Monocots Dicots How many cotyledons? How are the veins organized? Flower parts are in multiples of… Arrangement of vascular tissue is… Plant examples 14. Describe the three types of plant lifestyles. Chapter 21 Plant Structure and Function 15. Name and describe the 3 basic types of plant cells. 16. Name and describe the three types of tissue systems in plants. 17. What materials move through the xylem? 18. The ______________ __________________ theory proposes that water can rise through a plant due to (a)the tendency of hydrogen bonds to form between water molecules, called _______________________; and (b) the attraction of water molecules to the xylem wall, called _____________________________. These two forces create __________________________ that moves water upward in xylem. 19. Two other forces which aid movement of water in plants are ______________________ _____________________, which causes water to rise above ground level and loss of water from the leaves, which is called ______________________. 20. The theory describing how sugars move through the phloem is called the ____________ ________________ _____________. 21. The 3 steps in the model in #20 are…. (p606) 22. Name 4 things roots do for plants. 23. What are root hairs, and why are they important to plants? 24. What is the purpose of the root cap? 25. Draw a fibrous root and a tap root. 26. What is the difference between primary growth and secondary growth in plants? 27. How do guard cells work? Chapter 22 Plant Growth, Reproduction and Response 28. The type of life cycle, which alternates between diploid and haploid generations, is called _______________________ ______ ________________________. 29. The diploid phase begins with a ____________________ , which divides by _______________ and grows into a mature _________________________________. The sporophyte produces _______________ by _____________________. 30. The haploid phase begins with the spore dividing by ____________________ and growing into a mature ______________________________. These plants produce _________________________ through __________________. Then through fertilization, the cycle continues with a new ___________________________. 31. What are sepals? 32. Name the male parts of a flower. 33. Name the female parts of a flower. 34. What is pollination? 35. Another name for the male gametophyte of a flower is a _____________ ___________. 36. Where is the female gametophyte of a flower? 37. Describe double fertilization in flowers. 38. The 3N cell from double fertilization is called the ________________________, and is used for ___________________________________________________________. 39. The __________________ of the plant grows into a fruit. Fruits always have ______. 40. Name three ways seeds may be dispersed: 41. What is germination? What emerges first from the seed? 42. Why is seed dormancy important? 43. What is vegetative reproduction? 44. Fill out is following table regarding vegetative reproduction: Stolons Rhizomes Tubers Bulbs What and where is the stem? Give an example 45. What is a hormone? 46. Fill out the following chart on plant hormones: Gibberellins What do they do for plants? Give an example Ethylene Cytokinins Auxins 47. What is a phototropism? 48. Describe phototropism. 49. Describe thigmotropism. 50. Describe gravitropism. 51. What is photoperiodism?