Plant Processes Notes Photosynthesis Reaction how components of
advertisement

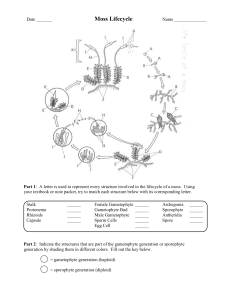
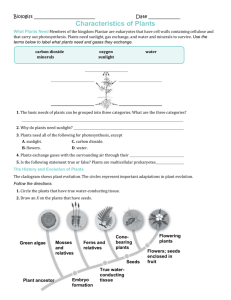
Plant Processes Notes I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. Photosynthesis a. Reaction how components of the reaction are acquired b. Location of reaction organelles involved Cellular Respiration a. Reaction how components of the reaction are acquired b. Location of reaction organelles involved Similarities between the reactions – p. 337 Differences between the reactions – p. 337 Tropisms = response by plant to a stimulus a. phototropism = response to light i. positive phototropism = towards light ii. negative = away from light b. thigmotropism = response to touch c. geotropism/gravitropism = response to gravity Photoperiodism = response by plant to the number of hours of darkness in its environment a. long-day plants = plants that flower because they have less than 10-12 hours of darkness b. short-day plants = require more than 12 hours of darkness to flower c. day-neutral plants = flowering is unaffected by the number of hours of darkness Plant hormones = substances acting as messengers that aid chemical reactions a. auxins = increase plant growth; typically in phototropism to elongate cell opposite of light source in order to cause the plant to bend to the light b. ethylene = gas produced by seed, fruit, leaves, & flowers; stimulates the ripening of fruit c. gibberellins = increases the rate of cell division and cell elongation d. cytokinins = increases the rate of cell division, especially in roots; slows aging of flowers and fruits Plant Reproduction a. Alternation of generations – all plants i. sporophyte stage = diploid ii. gametophyte stage = haploid b. Moss Life Cycle i. gametophyte stage occupies the largest portion of the life cycle 1. gametophyte = photosynthetic 2. gametophyte plants grow by mitosis from haploid spores 3. separate male and female plants ii. sporophyte stage begins with fertilization 1. sporophyte stalk grows by mitosis 2. stalk is not photosynthetic and relies on gametophyte for energy IX. 3. meiosis inside spore case produces haploid spore to start cycle over c. Fern Life Cycle i. sporophyte stage occupies largest portion of life cycle 1. fronds have sori that undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores 2. spores are catapulted into the air ii. spores germinate into microscopic gametophyte 1. prothallus = heart shaped gametophyte a. contains separate male and female areas that produce individual sex cells b. fertilization produces sporophyte beginning cycle again Seed Plant Reproduction a. seed, parts, & their function – p. 354 i. embryo ii. endosperm = food supply iii. seed coat b. pollen grains i. pollination c. gymnosperms – cone bearing plants i. cones – separate male and female cones ii. male cones – smaller or papery thin; produce pollen iii. female cones – usually larger; contain egg 1. fertilization forms zygote in female cone 2. become seeds d. angiosperms i. flower parts – p. 356 ii. life cycle – p. 357 e. seed dispersal mechanisms/methods