AP Biology Test Review: Protists, Fungi, and Plant Classification
advertisement

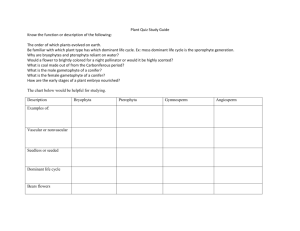
AP Biology Test Review: Protists, Plant Classification / Reproduction / Hormones PROTISTS: Handout USEFUL WORDS: Protist Phytoplankton Dinoflagellate Diatom Euglenoid Fruiting Body Slime Mold Cellular Slime Mold Fucoxanthin Plasmodium Pseudopod Pseudoplasmodium Protozoa Zooflagellate Sarcodine Amoebae Heliozoan Formaniferan Radiolarian Sporozoan Phycobilin Ciliate Gametophyte Spore Sporophyte 1) Explain how organisms in this kingdom differ from Monerans. 2) Describe the major divisions of protists. 3) Give the basic characteristics of dinoflagellates, diatoms, and euglenoids, and give an example of each. 4) Give the basic characteristics of fungus-like protists. 5) Give the basic characteristics of zooflagellates, sarcodines, sporozoans, and ciliates, and give an example of each. 6) Explain how eukaryotes may have evolved from a symbiotic relationship. 7) Discuss the characteristics of various groups of multicellular protists PLANT CLASSIFICATION: Handout USEFUL WORDS: Bryophyte Zygote Tracheophyte Vascular tissue Alternation of generations Homosporous Gametophyte Heterosporous Sporophyte Gymnosperm Tracheid Lignin Vein Leaf Sporangium Sorus Pollen Grain Pollination Embryo Seed Coat Cotyledon Flower 1) 2) 3) 4) Monocot Dicot Archegonium Antheridium Angiosperm Root Stem Cone Seed Fruit List the features common to all plants. Discuss adaptations that permitted plants to colonize land. Describe the differences between bryophytes and tracheophytes. Give characteristics and examples of bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. 5) Describe the differences between gymnosperm and angiosperms. 6) List features common to monocots and to dicots. 7) Explain the alternation of generations exhibited by plants. 8) Classify plants given identifying features. 9) Distinguish among homosporous and heterosporous. 10) Discuss the life cycle of bryophytes as compared to the life cycle of seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms and angiosperms. Identify structures responsible for the production of gametes or spores in each. Ch. 38 Angiosperm Reproduction USEFUL WORDS: Sporophyte Monoecious Gametophyte Dioecious Sepal Complete flower Petal Perfect flower Stamen Pollination Anther Double-fertilization Filament Hypocotyl Ovary Radicle Ovule Epicotyl Microspore Megaspore Vegetative propagation Fragmentation Apomixis Cotyledon Polar nuclei Endosperm Synergids 1) Outline the angiosperm life cycle. 2) Correctly label the diagram of a flower. 3) Distinguish between complete and incomplete, monoecious and dioecious, and perfect and imperfect flowers. 4) Explain where in the flower gametes are produced. 5) Describe the formation of pollen grains. 6) Describe the development of an embryo sac, and explain what happenes to each of its cells. 7) Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. 8) Outline the process of double fertilization. 9) Describe the function of endosperm. 10) Distinguish between sexual reproduction and vegetative propagation. 11) Give examples of vegetative propagation. Ch. 39 -- Plant Hormones USEFUL WORDS: Hormones Cytokinin Tropism Gibberellin Phototropism Abscisic Acid Auxin Ethylene Expansin Apoptosis Thigmotropism Long-Day Plant Critical Night Length Circadian Rhythm Day-Neutral Plant Photoperiodism Gravitropism Short-Day Plant Statolith 1) List five classes of plant hormones, describe their major functions, and recall where they are produced in the plant. 2) Explain how the ration of cytokinin to auxin affects cell division and differentiation. 3) Define apical dominance and describe the check-and-balance control of lateral branching. 4) Describe the effects of too much gibberellin on a plant. 5) Describe the antagonistic relationship between ABA and gibberellin. 6) Explain what is meant by a tropism, and give a few examples. 7) Distinguish among short-day plants and long-day plants.