Unit 4 Review KEY angiosperms - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

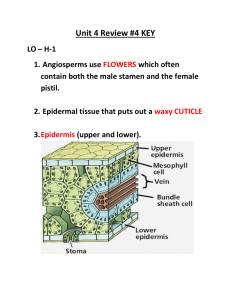
Unit 4 Review #4 KEY LO – H-1 1. Angiosperms use flowers which often contain both the male stamen and the female pistil. 2. Epidermal tissue that puts out a waxy cuticle. 3. Epidermis (upper and lower). 4. The palisade mesophyll is tightly packed columnar cells that are designed to trap solar energy. 5. These cells would be packed with CHLOROPLASTS. 6. Guard cells are responsible for opening and closing the stomata. To regulate water loss while allowing gas diffusion. 7. Stomata will be closed during the night time and during the extreme heat of the day. They open when they photosynthesize. 8. Guard cells open their stoma by drawing water into themselves. This occurs because as they photosynthesize they fill up with sugars. This high sugar concentration draws water in to swell up the guard cells. As they swell they bulge outward to open up the stoma. 9. The root cap is responsible for protecting the tip of the root, lubricating a pathway and by releasing Carbonic Acid to help create a pathway for the root. 10. In the Zone of Elongation, cells grow in size. 11. The Zone of Maturation/Differentiation. 12. Roots work hard to pump minerals from the soil into their cortex cells. These minerals set up a concentration gradient that then draws water in from one cell to the next, driving it all the way to the Xylem. 13. Water cohesion = Water molecules sticking to each other. - Water adhesion = Water sticking to other substances. 14. Pollen grains form on the ANTHER of the stamen. 15. Petals, nectar and pollen all attract pollinators. 16. Pollination is the process of moving pollen from the male anther over to the female stigma. 17. As the pollen tube grows, two sperm nuclei migrate down the tube. 18. Haploid EGG CELL Zygote EMBRYO 19. Diploid POLAR NUCLEUS ENDOSPERM 20. DOUBLE FERTILIZATION 21. A Seed includes : A) SEED COAT B) Embryo 22. C) Endosperm The OVARY 23. A complete flower has both female and male reproductive organs in the same flower. An incomplete flower has only male or female parts in one flower. 24. The advantages of incomplete flowers is that more variation will occur as better genetic blending is required between two different plants. 25. The big disadvantage with incomplete flowers is that they must have cross pollination, so if no other member of the same species is in that vicinity, they will not be able to sexually reproduce, therefore no seeds! 26. Angiosperms are mostly used for crops and foods and feeding to livestock. They are also used for hardwood furniture and flooring. LO H-2 Flower Parts LO – H2 1. Angiosperms hold and protect their seeds, Gymnosperms leave their seeds naked/exposed. Use flowers not cones. Angiosperms have Vessel Elements to strengthen and form a stronger Xylem (hardwood). Many Angiosperms use fruit for seed dispersal. LO – H-3 1. A cotyledon is the first embryonic seed leaf in a seed. It supplies food for developing seedling 2. Monocots have one cotyledon - Dicots have two 3. The veins in the leaves of monocots run parallel to each other. 4. MONO – SSPORRT - RR = Ringed pattern in the root of a monocot. - In a dicot, the xylem forms a star or “X’ with the phloem packed around. 5. THREE. 6. FOUR or FIVE 7. They form a ring in Dicots, while they are Scattered in the Stem of a Monocot. SSPORRT 8. Monocots include grasses, wheats, barley, rye, onion, corn, tulips, daffodils, garlic, lilies etc. 9. Dicots include tomato, pea plants, cherry trees, apple, pear etc.