Lewis Structures: Section 1.4
advertisement
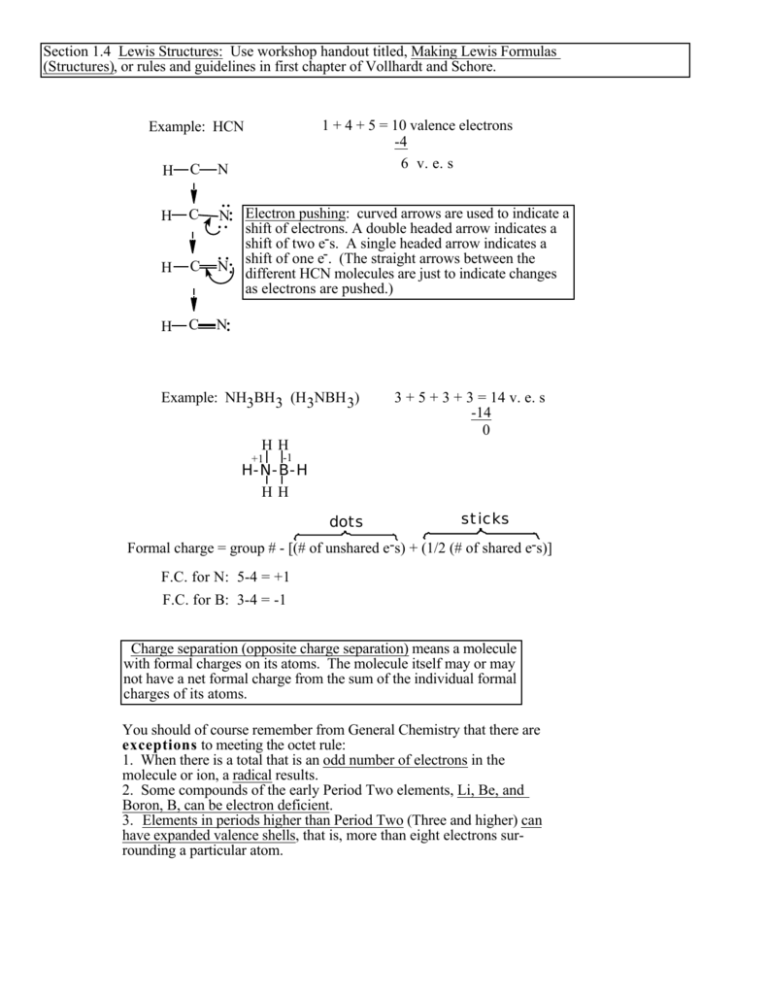
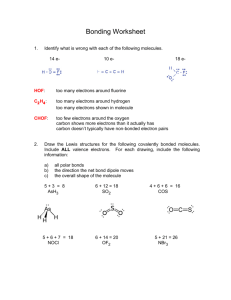
Section 1.4 Lewis Structures: Use workshop handout titled, Making Lewis Formulas (Structures), or rules and guidelines in first chapter of Vollhardt and Schore. 1 + 4 + 5 = 10 valence electrons -4 6 v. e. s Example: HCN H C N H C N H C N H C N Electron pushing: curved arrows are used to indicate a shift of electrons. A double headed arrow indicates a shift of two e-s. A single headed arrow indicates a shift of one e-. (The straight arrows between the different HCN molecules are just to indicate changes as electrons are pushed.) Example: NH3BH3 (H3NBH 3) 3 + 5 + 3 + 3 = 14 v. e. s -14 0 HH +1 -1 H-N-B-H HH dots sticks Formal charge = group # - [(# of unshared e-s) + (1/2 (# of shared e-s)] F.C. for N: 5-4 = +1 F.C. for B: 3-4 = -1 Charge separation (opposite charge separation) means a molecule with formal charges on its atoms. The molecule itself may or may not have a net formal charge from the sum of the individual formal charges of its atoms. You should of course remember from General Chemistry that there are exceptions to meeting the octet rule: 1. When there is a total that is an odd number of electrons in the molecule or ion, a radical results. 2. Some compounds of the early Period Two elements, Li, Be, and Boron, B, can be electron deficient. 3. Elements in periods higher than Period Two (Three and higher) can have expanded valence shells, that is, more than eight electrons surrounding a particular atom.