Nucleic Acids
advertisement

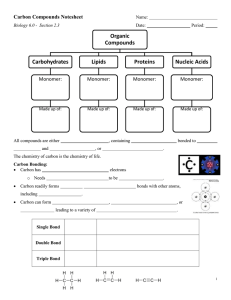
Carbon Compounds Notesheet Name: Biology - Section 2.3 Date: Period: Organic Compounds Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monomer: Monomer: Monomer: Monomer: Made up of: Made up of: Made up of: Made up of: All compounds are either , containing and , or bonded to . The chemistry of carbon is the chemistry of life. Carbon Bonding: Carbon has valance electrons o Needs electrons to be Carbon readily forms including . bonds with other atoms, . Carbon can form , leading to a variety of , or . Single Bond Double Bond Triple Bond 1 Large Carbon Molecules In many carbon compounds, the molecules are built up from smaller, simpler molecules known as . Monomers can bind to one another to form complex molecules known as . o Large polymers are also called o The process of reacting ____________________ molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks _____________ is the most important inorganic compound in the body and it participates in two important biological reactions Biological Reaction and Description of Process . Illustration of Process Hydrolysis Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation) Molecules of Life The four main classes of organic compounds essential to all living things are all made from ____________, _________________, and ____________________ atoms, but in different ratios giving them different properties. A. Carbohydrates Made of , , and with H to O in a ratio. o Monomers are called __________________________________ - a single sugar o Source of o Can be in or form o Ending for sugars: Glucose, galactose, and fructose all have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms = Molecular formula = ____________________ (hexoses) ____________________ (pentoses) 2 Type of Sugar Name of Monosaccharide Pentose Found in RNA Pentose Found in DNA Hexose In blood; cell’s main energy source Hexose In fruit; sweetest of monomers Hexose In milk Disaccharides are ____________ Description of Sugar ________________: Two monosaccharides to form o Formed by ____________________ synthesis (aka condensation reaction) o Molecular formula =_________________ Common Disaccharides Name of Disaccharide 2 single sugars that join to form the disaccharide Description of Sugar Table Sugar In milk In malt Polysaccharides _________ ____________________: General Formula - _______________ Formed by ____________________ ______________________ Long chains of __________________ molecules 3 Name of Polysaccharide Description of Sugar Glycogen Starch Cellulose B. Lipids Elements – , , and - NOT (H:0) energy than bonds o Do not dissolve in __________________ o Lipids contain a large number of _________ bonds which store in carbohydrates o Monomers: ______________________________ and ______________________________ Fatty acids are unbranched C-chains – (12-28 C) with a _____________ group ( ) at one end o The carboxyl end is ______________ and attracted to water o The hydrocarbon end is _________________ and doesn’t interact with water – List three major roles of lipids in living organisms: 1. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 4 Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids Saturated Fatty Acids Unsaturated Fatty Acids Lipids (fats, oils, and waxes) are formed by a molecule bonding to . Formed by ____________________ synthesis. 5 Complex Lipids Triglycerides Phospholipids C. Proteins Elements: Monomer: ____________ ________________ (20 different kinds) Each amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to 4 other atoms or functional groups , , , ________________ Bond that joins amino acids (protein) = _________________________ Formation of a peptide bond: 6 List five functions of proteins: 1. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Enzymes Enzyme + Substrate = ES complex = EP complex = Enzyme = product(s) Denaturing Proteins Protein that has lost its ________________________________, or __________________ Denaturing caused by: o ____________________________________ o ____________________________________ o ____________________________________ 7 D. Nucleic Acids Large, complex organic compounds that information in cells, using a system of compounds to store information, arranged in a certain order as a for genetic instructions of the cell. Elements: , , , , and __________________ Monomer: ________________________ 1. __________________________________ 2. __________________________________ 3. __________________________________ Nucleotides combine, in to form a double helix, and in The sides of the ladder are made up of the a single helix and the ______________ and the rungs of the ladder are Examples of Nucleic Acids: 1. 2. 8