Bio-Chemistry (AKA Organic Chemistry)
advertisement

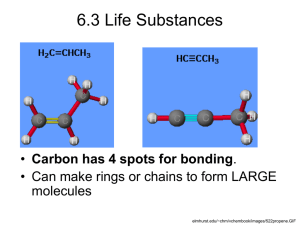
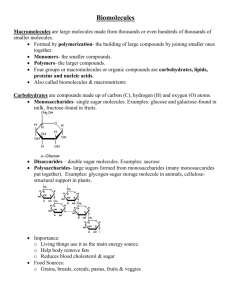
Inorganic Compounds: from minerals or nonliving source. Organic Compounds: contain Carbon & come from a living thing. Carbon can combine with other elements to form millions of compounds. Simplest Organic Compound is CH4 (Methane) VOCABULARY ALERT! Polymer: long chains of carbon molecules. Monomer: the building block of a polymer. Examples: A bead necklace = Polymer Individual Bead = Monomer Elements: C, H, O Ratio of H:O is 2:1 Building Blocks: Function: Monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose) Energy and storage molecules Examples: Monosaccharides – Glucose(C6H12O6) Disaccharides – lactose (in milk), sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharides – starch, cellulose, glycogen SIMPLE SUGARS (SUCROSE) STARCH (POTATO PLANTS STORE SUGAR IN THE ROOTS AS STARCH ) Elements: C, H, O Ratio of H:O is more than 2:1 Building Blocks: Fatty Acids Function: Energy storage Part of the Cell Membrane Examples: Beef Fat (C15H112O6) Oils, Wax OILS ARE LIQUID AT ROOM TEMPERATURE FATS ARE SOLID AT ROOM TEMPERATURE DIFFERENT KINDS OF FATS CELL MEMBRANE Elements: C, H, O, N, S Building Blocks: Amino Acids Function: Structural Molecules & Functional Molecules Examples: Muscle, skin, hair, fingernails Enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) FINGER AND TOE NAILS MUSCLE CELLS Elements: C, H, O, N, P Building Blocks: Nucleotides (a sugar, phosphate, & nitrogen base) Function: Stores and transmits hereditary info. Controls cell activity Makes proteins Examples: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) & RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)