Assistance Lecturer Amjad Ahmed Jumaa Nomenclature of the
advertisement

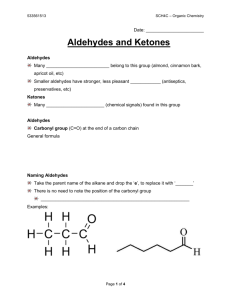
Organic and biochemistry Nomenclature of the aldehydes and ketones Reactions of the carbonyl compounds Esters. Assistance Lecturer Amjad Ahmed Jumaa www.soran.edu.iq 1 1-Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones: Aldehydes: 1-Common names: Are derived from the names of the corresponding carboxylic acids by replacing –Ic of the acids by –aldehyde. 2- IUPAC nomenclature: Follow the usual pattern, the longest chain carrying the –CHO group is considered the parent structure and is named by replacing the –e of the corresponding alkane by –al. the position of a substituent is indicated by a number, the carbonyl carbon always being considered as C-1. In the common name the (alpha) is corresponding to C-2 in the IUPAC name. Look at the following examples: www.soran.edu.iq www.soran.edu.iq Ketones: A ketone in which the carbonyl group is attached to a benzene ring is named as a –phenone, as illustrated below. the longest chain carrying the carbonyl group is considered the parent structure, and is named by replacing the –e of the corresponding alkane with –one. The positions of various groups are indicated by numbers, the carbonyl carbon being given the lowest possible number. www.soran.edu.iq www.soran.edu.iq 5 Problem: give the structure for the following ketones and aldehydes. 1-benzaldehyde. 2-(2-phenylbutanedial) 3-(benzylethylketone) 4-ethyl propyl ketone. Solution: www.soran.edu.iq Follow problem: determine the structures for the following aldehydes and ketones. 1-(dibenzylketone) 2-(benzophenone) 3-(5-hydroxybentanal) 4-(1-phenyl-1pentanol Reactions of carbonyl compounds: the carbonyl group, C=O, governs the chemistry of aldehydes and ketones. It does this in two ways: (a) By providing a site for nucleophilic addition, and (b) By increasing the acidity of the hydrogen atoms attached to the alpha carbon. www.soran.edu.iq The typical reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition reaction. 1-oxidation. Just for aldehydes. www.soran.edu.iq 8 Problem: write the structure and the name for the oxidation of furfural in the presence of K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, and H2O? Solution: Follow problem: predict the name and the structure for the resulting carboxylic acid form oxidation of the following aldehydes by using (K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O). 1-heptanal. 2-benzaldehyde 3-(para-tolualdehyde) 4-phenylacetaldehyde 5-formaldehyde. www.soran.edu.iq 2-addition of derivatives of ammonia. For both aldehydes and ketones. www.soran.edu.iq Example: Problem: give balanced equation for the following reaction in the acidic medium: 1-heptanal with hydroxylamine. www.soran.edu.iq 11 Solution: Esters: Closely related to the carboxylic acid and to each other are a number of chemical families known as functional derivatives of carboxylic acid. These derivatives are compounds in which the hydroxyl group –OH has been replaced by –OR' group. The general formula of the esters is: www.soran.edu.iq