Outline of Material Covered

ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
EXAM 2 MATERIAL REVIEW
I.
Chapter 14: NMR Spectroscopy
Origin of NMR absorption
Chemical shift values in 1 H NMR:
Local field (generated by electrons)
Shielding/Deshielding, High/Low Field
Induced magnetic field due to
-electron systems
Equivalent hydrogens – signals appearing at same chemical shifts
Enantiotopic and Diastereotopic hydrogens
Integration of signals
Spin-spin Coupling
Freely rotating systems; 3-bond distance between hydrogens; the “n+1 rule”
Complex coupling; systems where free rotation is restricted; the “(n+1)(m+1) rule”
II.
Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acids
Conjugation in carboxylates
Nomenclature
Acid-base equilibrium; why a particular side of the equilibrium is favored
Substituted benzoic acids; comparison of acidities
Phenols as acids
Separation of carboxylic acids and phenols from alcohols
III.
Chapter 20: Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry
The reactivity of the carbonyl group
Aldehydes/Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Nucleophilic addition versus nucleophilic substitution reactions to carbonyl compounds
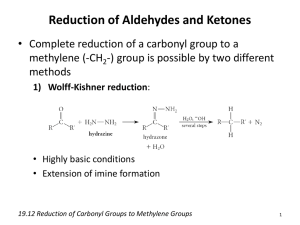
Hydride addition to aldehydes and ketones
Stereoselective hydride addition with the CBS reagent
Hydride substitution reactions of carboxylic acid derivatives
LiAlH
4
–substitution then addition
LiAlH[OC(CH
3
)
3
]
3
–only substitution: acid chloride to aldehyde
DIBAL-H –only substitution: ester to aldehyde
Organometallic Reagents
Organolithium Reagents: Preparation; Reactions with
1.
aldehydes and ketones (addition)
2.
acid chlorides and esters (substitution then addition)
Grignard Reagents: Preparation; Reactions with
1.
aldehydes and ketones (addition)
2.
esters (substitution then addition)
3.
epoxides
4.
carbon dioxide
Organocuprates: Preparation; Reactions with acid chlorides (to give ketones)
Metal acetylides
Organometallic Reagents as Bases
Synthesis with more than one functional group: Incompatible functional groups
A new synthetic Strategy: Protection – Deprotection
1.
Protection of a hydroxyl group by converting it into a silyl ethers
,
-unsaturated carbonyl compounds
Conjugate (1,4-type) additions with lithium cuprates
IV.
Chapter 21: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition
Oxidation Reactions (to form carbonyls) –Review Section 12.12
Reversible Additions to the Carbonyl Group
Cyanide addition – Cyanohydrin formation
Water addition –Formation of Hydrates
Alcohol addition –Formation of hemiacetals
Special Nucleophiles (phosphorus ylides): The Wittig Reaction (Section 21.10: 21.10A to 21.10D)