Assistance Lecturer Amjad Ahmed Jumaa IUPAC names of
advertisement

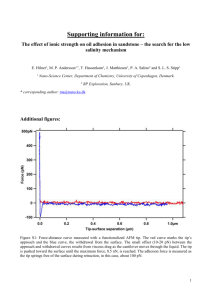
Organic and biochemistry IUPAC names of carboxylic acids Reactions of the carboxylic acids Aldehydes and ketones Assistance Lecturer Amjad Ahmed Jumaa www.soran.edu.iq 1 Nomenclature of the carboxylic acids: 1-Common names: oAliphatic carboxylic acids: The common names of the most important acids are coming from their sources rather than to their chemical structure. And sometimes depending upon the numbers of carbon atoms. We see the branched-chain and substituted acids are named as derivatives of the straight-chain acids. To indicate the position of the attachment, the Greek letters, -α; -β; -γ; -δ, etc. is used. The α-carbon is the one bearing the carboxyl group. Look at the following examples: www.soran.edu.iq Aromatic carboxylic acids, ArCOOH, are usually named as derivatives of the Parent acid, benzoic acid, C6H5COOH. The methyl benzoic acids are given the Special names of toluic acids. Look at the following examples. www.soran.edu.iq 3 IUPACnomenclature: Follow the usual pattern, the longest chain carrying the carboxyl group is considered the parent structure, and is named by replacing the –e of the corresponding alkane with –oic acid. For example. www.soran.edu.iq Problem: for the following carboxylic acid give the common names and IUPAC names: www.soran.edu.iq Solution: Ethanoic acid, acetic acid; (2-hydroxy-2-phenylethanoic acid), mandelic acid; benzenecarboxylic acid, benzoic. (o-hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid), salicylic acid. (1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid), phthalic acid. Follow problem: give the structure for the following carboxylic acids: 1-(α-bromo acetic acid) 2-(p-hydroxy acetic acid) 3-(p-toluic acid) 4-(m-chloro benzoic acid) 5-valeric acid. Give the names for the following carboxylic acids : 1) m-NO2C6H4CO2H 2) p-ClC6H4COOH 3) p-MeC6H5CO2H 4) CH3CH2CH2CO2H www.soran.edu.iq 6 Reactions of carboxylic acids: The characteristic chemical behavior, is determined by the functional group, carboxyl, -COOH, this group is made up of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH). Actually (-OH) undergo loss of (H+) or replacement by another group. 1-acidity. Salt formation. Example: www.soran.edu.iq Problem: write an ionic equation for the reaction of acetic acid with sodium ethoxide? Solution: www.soran.edu.iq Follow problem: give an ionic equation for the reaction of: 1-(p-bromobenzioc acid). 2-(α-methyl butyric acid). With the following inorganic bases: 1-sodium bromide. 2-sodium methoxide. 3-potassium tret-butoxide. 2-conversion into functional group. www.soran.edu.iq 9 Conversion into acid chloride Examples: www.soran.edu.iq Problem: write a chemical equation for the reaction of m-methoxyphenylacetic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) under heat condition. Solution: Follow problem: give an equation for the reaction of the following carboxylic acids with phosphorus trichloride. 1-pentanoic acid. 2-(m-aminobenzoic acid) 3-(2-methylbutanoic acid) www.soran.edu.iq Carbonyl compounds: Aldehydes and ketones: Aldehydes are compounds of the general formula RCHO; ketones are compounds of the general formula RR'CO. The groups R and R' may be aliphatic or aromatic. Both aldehydes and ketones contains the carbonyl group, C=O, and are often referred to collectively as carbonyl compounds. It the carbonyl group that largely determines the chemistry of aldehydes and ketones. www.soran.edu.iq