Option E2 Perception of Stimuli
advertisement

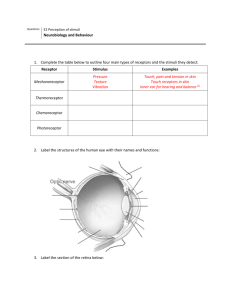
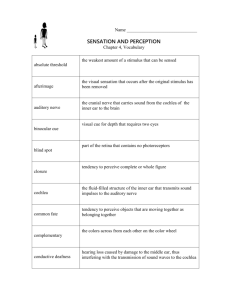
Option E2 Perception of Stimuli Assessment Statements: E.2.1 Outline the diversity of stimuli that can be detected by human sensory receptors. E.2.2 Label a diagram of the structure of the human eye. E.2.3 Annotate a diagram of the retina to show the cell types and the direction in which light moves. E.2.4 Compare rod and cone cells. E.2.5 Explain the processing of visual stimuli, including edge enhancement and contralateral processing. E.2.6 Label a diagram of the ear. E.2.7 Explain how sound is perceived by the ear Human Sensory Receptors Complete the table: Receptor Stimulus Location Mechanoreceptor Chemoreceptor Thermoreceptor Photoreceptor The Human Eye Label the diagram: Match the structure to its function: Structure Function Sclera Photoreceptive tissue and neurons of the eye Choroid Mucus secreting epithelia that provides moisture to the eye Retina Jelly like filling of the anterior section of the eye Fovea Coloured part of the choroid layer that regulate the light entering the eye Blind spot The collection of nerves from the photoreceptors Optic nerve Tough white outer layer of connective tissue Vitreous humour Transparent layer formed from the sclera, focuses the light Aqueous humour High concentration of cone cells and centre of field of vision Lens Thin pigmented layer that absorbs scattered light in the eye Iris Hole in the centre of the iris through which light reaches the retina Pupil Region of no photoreceptors where axons of neurons leave the eye Cornea Jelly like filling of the posterior cavity of the eye Conjunctiva Transparent protein disc suspended from ligaments, for fine focus The retina Label the diagram: Rods and Cones Complete the table: Feature Rods Cones Location in retina Optimal light conditions Visual acuity (resolution) Connection to nerve fibre Colour sensitivity Type of vision Number of types Relative abundance Define: Edge enhancement Contralateral processing What do you see? Explain this optical illusion: The Ear Add labels to the diagram: How Sound is Perceived Rearrange the sentences to describe how sound is perceived: Movement of the cochlear fluid affects the position of cilia on sensory hair cells. The ossicles push against the oval window, The degree of vibration will vary according to the frequency Sound travels as pressure waves in the air displacing fluid within the cochlea. transmitted via the auditory nerve to the brain. and amplitude of the sound waves. which magnify the vibrations up to 20 times. Cilia on hair cells vary in length and each resonates to a different frequency of sound. which push the membrane of the eardrum causing it to vibrate. Activation of the hair cells generates nerve impulses which are The kinetic motion of the cochlear fluid is dissipated by the movement of the round window. The ear drum pushes on the bones of the middle ear (ossicles) 1. List two groups of sensory receptors, giving the stimulus each perceives (2) 2. Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons and motor neurons in the response of animals to stimuli (3) 3. Label structures I to IV (4 marks) 4. Outline contralateral processing of visual stimuli (3) 5. Compare the functions of rod and cone cells (3) 6. Identify structures A to D (2) 7. Explain how sound is perceived by the ear (6)