File
advertisement

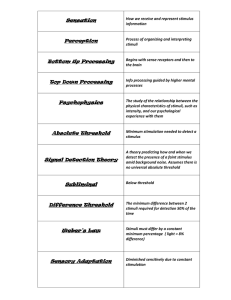
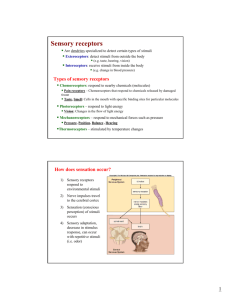
Name _______________________________ SENSATION AND PERCEPTION Chapter 4, Vocabulary the weakest amount of a stimulus that can be sensed absolute threshold afterimage the visual sensation that occurs after the original stimulus has been removed auditory nerve the cranial nerve that carries sound from the cochlea of the inner ear to the brain visual cue for depth that requires two eyes binocular cue part of the retina that contains no photoreceptors blind spot tendency to perceive complete or whole figure closure cochlea the fluid-filled structure of the inner ear that transmits sound impulses to the auditory nerve common fate tendency to perceive objects that are moving together as belonging together the colors across from each other on the color wheel complementary conductive deafness hearing loss caused by damage to the middle ear, thus interfering with the transmission of sound waves to the cochlea continuity the perceptual tendency to group stimuli into continuous patterns difference threshold the minimum amount of difference that can be detected between two stimuli gate theory the suggestion that only a certain amount of information can be processed by the nervous system at a given time kinesthesis the sense that provides information about the position and movement of individual body parts transparent structure of the eye that focuses light on the retina lens cue for distance that may be available to either eye alone monocular cue olfactory nerve the nerve that transmits information about odors from olfactory receptors to the brain perception psychological process through which we interpret sensory stimulation a neuron that responds to light photoreceptor proximity the perceptual tendency to group together visual and auditory events that are near each other opening in the colored part of the eye pupil retina light-sensitive inner surface of the eye that contains the rods, cones, and neurons that process visual stimuli retinal disparity a binocular cue for perceiving depth based on the difference between the two images of an object that the retina receives as the object moves closer or farther away sensation stimulation of sensory receptors and the transmission of sensory information to the central nervous system deafness that results from damage to the auditory nerve Sensori-neural deafness sensory adaptation process by which we become more sensitive to weak stimuli and less sensitive to unchanging stimuli signal-detection theory method of distinguishing sensory stimuli that takes into account not only their strengths, but also such elements as the setting, mood, etc. similarity the perceptual tendency to group together elements that seem alike stroboscopic motion a visual illusion I which the perception of motion is generated buy the presentation of a series of stationary images in rapid succession vestibular sense the sense that provides information about the position of the body keenness or sharpness of vision visual acuity