E2 Questions
advertisement
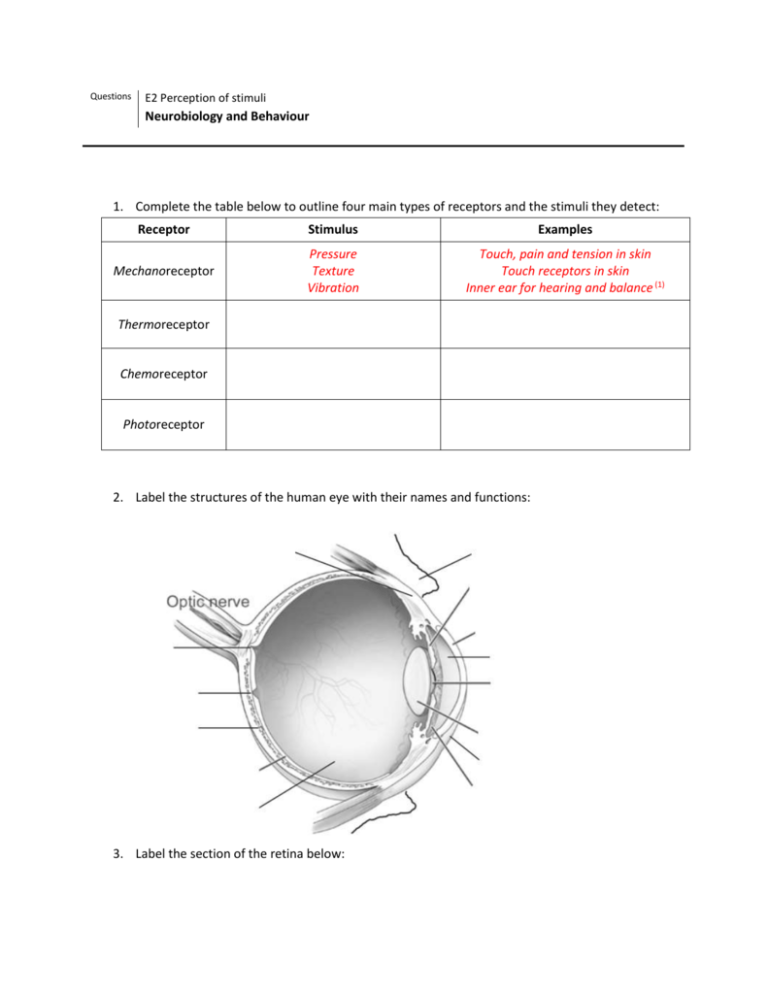
Questions E2 Perception of stimuli Neurobiology and Behaviour 1. Complete the table below to outline four main types of receptors and the stimuli they detect: Receptor Stimulus Examples Mechanoreceptor Pressure Texture Vibration Touch, pain and tension in skin Touch receptors in skin Inner ear for hearing and balance (1) Thermoreceptor Chemoreceptor Photoreceptor 2. Label the structures of the human eye with their names and functions: 3. Label the section of the retina below: 4. Annotate the diagram below to outline how light stimulus is received by the photoreceptor and converted to an action potential: 5. Compare rod and cone cells: Rod cells Cone cells Light brightness Diversity of cells Wavelength sensitivity Impulse: neuron ratio distribution 6. Explain how visual stimuli are processed in the eye and brain, with reference to the following stages (you can draw or find images to help, if you wish): a. Image focusing and inversion in the cornea and retina b. Visual fields c. Contralateral processing and the role of the chiasma d. The role and location of the visual cortex in the brain e. Edge enhancement and ‘filling in’ of the blind spot 7. Label the diagram with the structures of the ear, and use the diagram to explain how sound is perceived by the ear. Further thought: 1. How does colour blindness work, from both a genetic and neurological perspective? 2. What are risk factors in hearing and vision loss and how can they be mitigated? 3. Research the use of stem cells and gene therapy in restoring vision to those who have been blinded or who have blindness due to genetic factors.