Chambers
advertisement

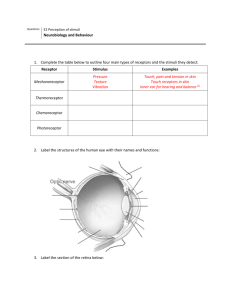
Memmler’s A&P Chap 11 The Sensory System Sensory system p236 • • • • • Receives stimuli Initiates nerve impulse Sensory receptors Special senses General senses •Structure of the eye •tunics •Sclera •Choriod •Retina •Chambers of the eye •Anterior chamber •Posterior chamber Eye p236 Protection for the eye p 236-237 Skull Eyelids Eyelashes Eyebrows Conjunctiva Tears Pathway of light thru the eye p237 • Refraction • Path of light: – Cornea – Aqueous humor – Lens – Vitreous body – Light is focused on retina at the fovea centralis The Retina 238 – Rods – Cones Extrinsic muscles p239 •Allow the eyes to move Intrinsic muscles p240 •Form the iris and the ciliary muscle Accomodation p241 Function of the iris p 240 Errors of refraction/eye disorders p242 • • • • • • • • • • Hyperopia Myopia Astigmatism Strabismus Cataract Glaucoma Macular degeneration Retinopathy Retinal detachment Presbyopia The Ear •Sections: •Outer ear •Middle ear •Inner ear p245 Ossicles p 245 Inner ear p246 Disorders of the ear p247 • • • • Otitis media Otitis externa Hearing loss: conductive or sensorineural Presbycusis Sense of taste p249 • Gustation • Taste buds located on tongue • Taste contributes to appetite Sense of smell p250 • Olfaction • Receptors located in epithelium of upper nasal cavity • Smell contributes to appetite Sense of touch • Tactile corpuscles are located in dermis of skin p250 Sense of pain p252 • Widely distributed free nerve endings • 2 pathways for pain transmission to brain – Acute, sharp pain – Slow chronic pain Sense of position p251 • Proprioceptors: Receptors located in muscles, tendons, joints relay impulses to the brain (cerebellum) Sensory adaptation 253 • When sensory receptors are exposed to a continuous stimulus, receptors often adjust themselves so that the sensation becomes less acute.