Sensation 201
advertisement

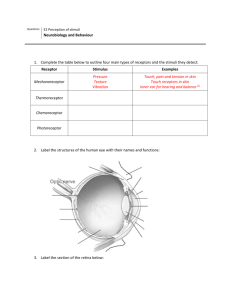
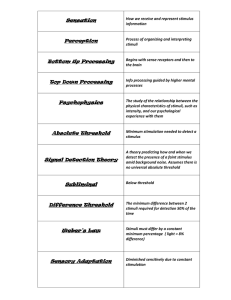
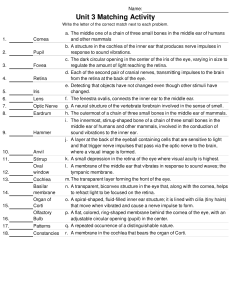
Vision & Audition Page 20 October 15, 2010 Stimuli Distal: as in the environment Proximal: as on the retina The Biology Cornea: protection Lens Curvature accommodates for dist. Retina Cones: center – code for color Rods: periphery – dark, movement Optic Nerve Transmits images to both hemis. Occipital Lobe Perceives images based on color, movement, depth, & form Trichromatic Theory • aka Young-Helmholtz Theory • Cones interpret stimuli in blue, red & green frequencies Opponent Process Theory • Thalamus codes for Black or White Red or Green Blue or Yellow • Afterimage • Colorblindness Stimuli • 0 decibels (20 Hz) • 150 decibels (20,000 Hz) The Biology • Outer Ear Pinna: channel sound waves • Middle Ear Tympanic Membrane Sound waves vibrate the ear drum Malleus (Hammer), Incus (Anvil), Stapes (Stirrup) Amplify vibrations • Inner Ear Cochlea: home to neurons Auditory Nerve Transfer message brain • Temporal Lobe Perceives auditory stimuli Georg von Bekesy (1961 – Nobel Prize) • The cochlea interprets sound wave frequencies • Higher frequencies stimulate more neurons Place Theory • Different “places” along the cochlea activated • Problem: < 4,000 Hz Frequency Theory • Pitch determined by the frequency of sound waves • Problem: differences of >1,000 Hz • Volley Principal: alternate firing of neurons Conductive Deafness • Injury to the outer or middle ear • Treatment: medication, surgery, or hearing aid Sensorineural (Nerve) Deafness • Injury to the inner ear • Treatment: hearing aides or cochlear implant