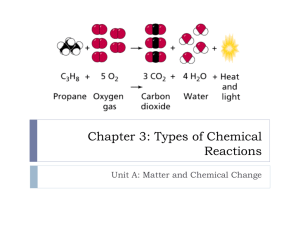
Chemical Reactions

Chemical Reactions
Words that indicate chemical reactions:
1.
_____________________
2.
_____________________
3.
_____________________
4.
_____________________
Chemical Reactions
• Occur when ____________________________________________________________________
• Indicators:
– Formation of __________, _____________, or release of __________________.
• Reactants ________________________
• ____________________ are on the left of the arrow
• ____________________ are on the right of the arrow
• ____________________ = yields, gives, reacts to produce
• Chemical Reactions always involve changes in __________________________
Energy and Reactions
• Energy must be added to ______________________________________
• Forming bonds _____________________ energy
• Energy is _________________________ in chemical reactions
Laws of Conservation
Mass o Matter can neither be ______________________ nor ______________________
Energy o Energy can neither be ______________________ nor ______________________
Energy and Reactions
• Reactions that release energy are called ________________________ Reactions
• Reactions that absorb energy are called ________________________ Reactions
1
Chemical Reactions
Chemical Equations
• Representation of a __________________________________
• Fe + O
2
Fe
2
O
3
{___________}
• ______________________ ______________________
Balancing Equations
What is wrong with the following equations?
H
2
+ Cl
2
HCl ___H
2
+ ___ Cl
2
___ HCl
Mg + O
2
MgO
C
2
H
6
+ O
2
CO
2
+ H
2
O
___ Mg + ___ O
2
___ MgO
___ C
2
H
6
+ ___ O
2
___ CO
2
+ ___ H
2
O
2
Balanced Equation
• A balanced equation ___________________________________________
• Law of definite proportions:
– A compound always contains the ____________________________ in the
________________________________ regardless of how the compound is made or how much of the compound is formed.
Balancing Equations
• __H
2
+ __O
2
__H
2
O UNBALANCED
Chemical Reactions
Chemical Reactions – 5 Types
Synthesis
• A reaction in which _______________________________________________________________
• A.K.A. : ________________________ or __________________________
• General Equation
____+ ____ _______
• EX: 2 Li + Se ---> Li
2
Se
Decomposition
___________ reactant breaks down into _____________________________ products
General Equation: _______ ____+ ____
Ex: 2 HgO 2 Hg + O
2
Combustion
One or more reactants combine with ______________ releasing _______________ or
_____________ o Any ____________________ reaction must include the reactant oxygen, O
2 o General Equation: A + O
2
AO o Ex: 2Mg(s) + O
2
(g) 2MgO(s)
Single Replacement
• A.K.A.: _______________________________
• One element _____________________ a similar element in a compound
• General Equation: ______+ ______ ______+ ______
• Ex: 2 Na + 2 HOH ----> 2 NaOH + H
2
Double Replacement
• Reaction that has the interchanging of two ____________ from two different compounds.
• general form: ______ + ______ ______+ ______
• Ex: Pb(NO3)2 + 2 KI ----> PbI2 + 2 KNO3
3
Chemical Reactions
• Equation consists of two reactants that have both a _________________ and
_________________.
• During a reaction the cations (or anions) ____________________________________.
• The products usually consist of a ____________________________.
Chemical Reaction Checklist:
• 1) Is O
2
a reactant?
– _____________________________
• 2) One product?
– _____________________________
• 3) One reactant?
– _____________________________
• 4) Is an element being replaced?
– _____________________________
• 5) 2 switches?
– _____________________________
4